Inboxes are awash with spam emails that cause productivity issues and potentially pose security threats. An email anti-spam server is a mail server that incorporates an email filtering solution to increase the server’s spam detection rate and reduce an organization’s exposure to email threats such as phishing, malware, and ransomware. Spam is a significant challenge for companies worldwide, flooding inboxes, hindering productivity, and posing security risks. An email anti-spam server integrates a filtering solution to improve spam detection and protect organizations from email-based threats like phishing, malware, and ransomware.
An email spam server can be created by installing an email filtering solution as a virtual appliance or redirecting the mail server's MX record to a cloud anti-spam service from a SaaS provider that deploys spam and phishing detection. However, spam detection is not an on/off switch; some anti-spam servers are better than others. We explore what features the best anti-spam server solution for your organization must offer.
Basics of how an anti-spam server works
An anti-spam server sits as a layer atop a mail server, like a guard checking the incoming and outgoing emails for legitimacy and security. As such, the server spam solution is configured to filter incoming emails at the server level rather than at the client level. Consequently, an email spam server has a much lower maintenance overhead than a client-based solution.
An anti-spam server solution uses multiple layers of protection to ensure the fine-grained filters needed to identify sophisticated spam. These layers include Real-time Blackhole Lists (RBLs), Heuristics to examine code, antivirus engines, real-time URL checks, and Bayesian analysis for advanced checks.
Additional features include sandboxing to place suspicious emails into a safe environment for further analysis and greylisting.
An anti-spam server gives network administrators a higher level of governance over email activity and the volume of threats being blocked by the server.
The problem of spam, phishing, and the SMB
Phishing and spam are becoming increasingly sophisticated. GenAI tools like ChatGPT have allowed cybercriminals to generate highly believable and tailored content that is difficult for employees to identify as suspicious. Cybercriminals couple sophisticated phishing with automation to scale up the attacks, creating a deluge of AI-generated phishing emails. Cybercriminals target small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) as they are less likely to have advanced tools and security know-how in place. As a result, SMBs are at high risk of damage from spam and phishing:
- 94% of small business owners experienced data breaches or cyberattacks.
- Phishing is the initial attack vector in 41% of ransomware attacks.
- A ransomware attack would result in 75% of SMBs going out of business within five days of the attack.
- Another study found that 78% of SMBs are concerned that cyber-attacks would put them out of business.
Added:
Added:
Added:
Did You Know?
99.99%
SpamTitan's spam catch rate
11 Seconds
a ransomware attack occurs
$285
the average cost to manage spam per person without an email filter
56.50%
of all email is spam
Why add an anti-spam server to a mail server?
An email filtering service protects against cyber threats and prevents advanced phishing and spam-containing malware (malspam) from reaching users' inboxes. An advanced spam email service identifies potentially dangerous emails. The spam service then rejects or quarantines these emails. The spam service is superfast and sends legitimate emails to the recipient without delay. In an era where a single click on a carefully crafted link in the body of an email or the opening of a malicious attachment can lead to a ransomware attack, it is essential to have this layer of protection.
Some mail servers may come ready and configured to deliver basic spam protection levels. However, this essential protection is typically not robust enough. Cybercriminals continually modify their techniques and tactics to evade detection by conventional and basic anti-spam servers. Advanced malware variants are constantly released, and conventional signature-based detection methods struggle to block new malware threats. To address this security gap, third-party email filtering solutions have created advanced features and spam detection mechanisms that work alongside the default anti-spam servers built into some email platforms.
These advanced spam email services are significantly better at detecting sophisticated spam email and other threats. An additional layer of spam protection from an advanced spam email service ensures a robust security posture. With an advanced server spam filter or cloud-based filtering service, you will minimize the volume of spam emails that arrive in inboxes and block malicious messages before they cause harm.
How an email spam server achieves higher detection rates
Most default email services block spam using Real-time Blackhole lists (RBLs). These methods compare the IP addresses of incoming emails against databases listing IP addresses from which spam is known to have originated. A spam email likely evades detection at this point because it originated from a source not previously used for spamming. This disconnect is one of the main reasons conventional spam filters allow spam and phishing through.
An advanced email spam filtering server uses other functions to stop evasive spam, including the following:
Greylisting
One of the methods used in advanced server spam solutions is greylisting, which is used to identify spam sent from unknown sources. Greylisting works by returning suspicious incoming emails to the mail servers from which they originated, along with a request for the email to be resent. Most mail servers respond within minutes to return the email.
A cybercriminal's spam mail server will usually be too busy sending out spam emails to respond to resend requests, so spammers often switch off the resend option. Using this process to prevent spam from previously unknown sources, an email spam server increases the spam detection rate from 99% to close to 100%, substantially reducing the volume of sophisticated and dangerous messages delivered to employees' inboxes.
Once an email is returned, it undergoes a series of secondary tests to determine its authenticity. Greylisting can result in a short delay in receiving messages, which is why it is an optional control in SpamTitan. However, greylisting is highly effective as a layer of protection, so it is recommended. To avoid unnecessary delays, trusted senders can be added to an allowlist to ensure their messages are always delivered without delay.
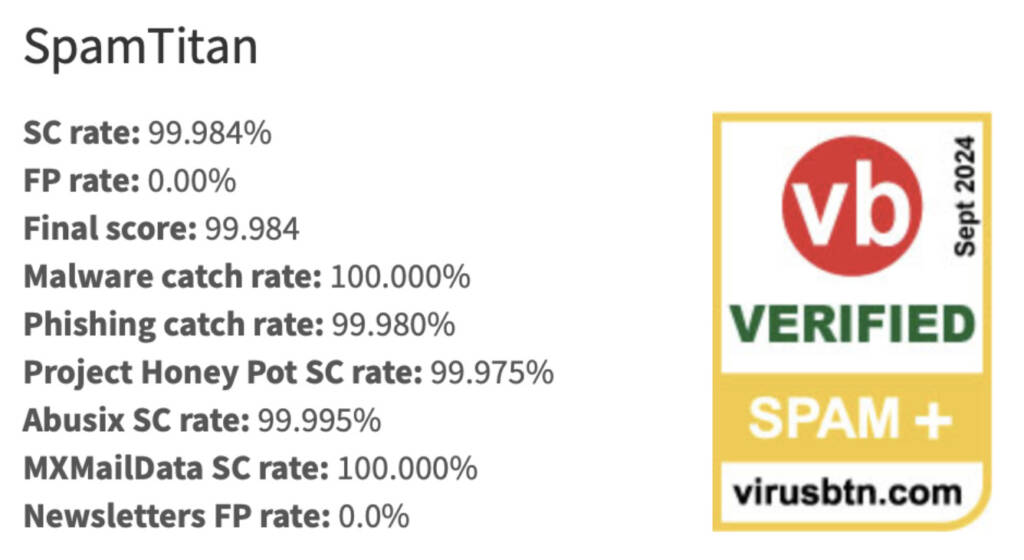
SpamTitan has been verified by Virus Bulletin as having a block rate of 99.98%.
Malicious URL interception
Detection of malicious URLs in real time can help prevent a phishing attack. Malicious URL inspection checks a link in an email in real time as the user clicks on the URL. The destination URL has multiple dynamic checks performed by the system, rather than the employee, following redirects to identify spoofed and malicious websites. Notably, SpamTitan Plus extends the protection of malicious link checks, using time-of-click analysis to protect against links to websites that appear to be safe on delivery but are later weaponized with malware.
Sandboxing
Sandboxing adds an additional control measure to the spam identification process. It isolates files suspected of being malware and safely analyzes them in the sandbox environment. Within the sandbox, an administrator can open emails, check malicious links, and use anti-malware tools to test for malware. The email can be forwarded to the original recipient if it is safe. The sandbox keeps track of any identified malicious signals, adding them to known attack types so that any repeat attacks will be automatically stopped.
A layered approach to spam: Defence in Depth
Cybercriminals develop spam and phishing emails to evade detection. It is an ongoing battle to keep up with the evolving evasive tactics, which means that a spam server must use layers of measures to adapt and predict them. Advanced spam servers must use intelligent measures to handle evasive and emerging threats. Some of the techniques used by a spam gateway, like SpamTitan Plus, include dual antivirus software, Bayesian analysis, real-time blocklists (RBLs), sandboxing, lists of websites that were detected in unsolicited emails (SURBLs), and sender policy frameworks. These layers add increasingly adaptive techniques to capture almost 100% of spam emails.
Hear from our customers
SpamTitan: An advanced anti-spam server solution
Email filtering solutions from SpamTitan use advanced mechanisms to reduce the volume of spam. Measures are multi-layered, including greylisting, sandboxing, Bayesian analysis, and SURBL analysis. When a greylisted email is returned, the SpamTitan email server solution runs a Sender Policy Framework test, HELO test, Reject Unknown Sender Domain test, and DMARC verification to authenticate incoming emails. These layers of fine-grained checks ensure that 99.98% of spam and phishing is stopped before it enters a user's inbox. However, real-time URL checks also prevent the inadvertent click of a malicious URL to set off a chain of events, leading to credential compromise and malware infection.
SpamTitan eliminates the inadvertent blocking of business-critical emails by allowing granular control over the acceptable spam thresholds. This is done on a user or group basis to ensure the service meets the requirements across the business.
An example of the usefulness of controllable spam thresholds
A sales department receives sales leads by email from miscellaneous sources. In this scenario, a system administrator could relax the acceptable spam threshold for employees within the sales department while maintaining a high threshold for the rest of the business. It is also possible to apply acceptable use thresholds by domain, if required, and add trusted domains to an allowlist to prevent a delay in the receipt of business-critical emails.
Despite the additional mechanisms and tools, SpamTitan is one of the most straightforward email filtering solutions to set up and use. Our spam email service is managed via a web-based administration portal with an intuitive interface. System administrators can apply and adjust the filter´s parameters with the click of a mouse from any Internet-connected device. It is also possible to schedule quarantine reports at any time of the night or day.
SpamTitan Dashboard (below)
SpamTitan Dashboard (above)
SpamTitan Statistics Dashboard (below)
SpamTitan Statistics Dashboard (above)
SpamTitan offers Defence in Depth against malicious emails
The most effective way of improving email security is through Defense in Depth, based on layered defenses. By relying on multi-layered security, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, protecting the company against rapidly evolving malware variants and sophisticated new phishing tactics.
Defense in depth or layered security is achieved by implementing unified layers of protection to secure assets. The watchwords of this approach are prevention, detection, and response.
A layered approach is much more effective than one large security platform, but it must be done correctly. All security layers must be unified and work together seamlessly. This can be a challenge when purchasing layers from multiple vendors. TitanHQ specializes in the various aspects of email security and delivers a unified multi-layered email spam and phishing server.
With a solution based on a layered approach, a business has access to comprehensive data sets, alerts, and monitoring. Extensive reporting provides better insights to strengthen your ability to secure your network. If one of the layers fails, the next comes into play to catch anything suspicious. Multiple layers are critical for a strong defense and quick containment.
Predictive methods for detecting new threats
SpamTitan uses several predictive methods for detecting new threats, such as subjecting each incoming message to a Bayesian analysis. Machine learning and heuristics also help significantly improve spam detection rates and prevent malicious and unwanted messages from reaching users' inboxes.
SpamTitan includes a Bitdefender-powered sandboxing feature to identify malicious code, zero-day malware, and ransomware threats. This feature protects against breaches and email attacks by providing a safe environment to run in-depth, sophisticated analyses of suspicious programs and files.
When email attachments pass the checks performed by the dual antivirus engines yet are suspicious, they are sent to the sandbox for in-depth analysis. The sandbox allows the files to be studied for malicious actions, such as Command and Control (C2) center callbacks. Without this feature, new malware variants would not be detected as malicious and arrive in inboxes.
A comparison of Office365 and SpamTitan
Email services provide a degree of protection against spam and malicious emails, but many threats slip through the net. Organizations that add an additional layer to their email defenses and adopt a third-party spam filtering solution will achieve far greater spam detection rates.
Office 365 Exchange Online Protection (EOP) has many built-in security features; however, organizations that have grown accustomed to dedicated security solutions with advanced filtering and advanced reporting capabilities are likely to find that the default security offering of Office 365 Exchange Online Protection (EOP) falls short of requirements. To obtain the same level of protection as a third-party specialist anti-spam server, like SpamTitan, a company would have to upgrade to the more expensive Microsoft Defender license.
SpamTitan’s spam detection rate has been independently verified and shown to block 99.98% of spam emails. This is achieved using advanced spam detection mechanisms such as SURBL filtering, machine learning, Bayesian analysis, and greylisting. SpamTitan also uses a variety of malicious URL detection mechanisms to detect phishing emails, and dual anti-virus software engines are used to detect and block malware and ransomware threats. The result is enhanced spam detection and more reliable blocking of spam, phishing emails, zero-day attacks, and new malware and ransomware threats.
| Microsoft Office 365 Exchange Online Protection (EOP) | SpamTitan | |
|---|---|---|
| Protection against emerging threats like zero-days | No | Yes |
| Greylisting | No | Yes |
| Basic attachment sandboxing | Yes | Yes |
| URL checking, including post-delivery | No | Yes |
| Advanced AR code detection | No | Yes |
| Multiple antivirus scanning | No | Yes
Uses dual AV scanning to improve detection rates |
| Advanced BEC (Business Email Compromise) prevention | No | It uses advanced AI-powered techniques like Natural Language Processing (NLP) to identify anomalous content and behavior. |
| Contextual warning tags on suspicious emails | No | Yes |
| Outbound email checks for spam signals | Yes | Yes |
| Operating system agnostic? | No | Yes |
| DMARC compliance of transactional email via DKIM-signing | No | Yes |
| Auto-remediation | Microsoft Defender only | Yes |
| Training offered | Limited to videos and documents | An array of options, in-person, videos, online, webinars, etc. |
Find out how to have your spam email service with SpamTitan
If you would like to find an effective way to reduce the volume of spam-evading detection and better protect your network against phishing, malware, and ransomware, speak with us about creating an email spam server with SpamTitan protection.
Our team of Sales Technicians will be happy to answer any questions you have about maximizing the spam detection rate and the features of SpamTitan that can help enhance network security.
Our team will also invite you to take a free trial of SpamTitan so you can evaluate the merits of an email spam server in your environment. The trial will allow you to find the appropriate spam threshold levels for each department in your business so that, should you choose to continue using our service at the end of the trial, no further configuration of the email filtering solution will be necessary.
- Cybercriminals and spammers are becoming more sophisticated.
- Standard email filters only block spam from previously known sources.
- The SpamTitan email filter can be configured to block spam from new sources.
- Different acceptable spam thresholds can be applied per user or user group.
- The email spam server can be administered from any Internet-connected device.
Please take advantage of our free trial offer to experience the benefits of SpamTitan today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I improve my Office 365 spam filter?
The best way to improve the Office 365 spam filter is to add a layer of protection on top with a third-party solution such as SpamTitan. A third-party spam filter doesn’t replace the spam and phishing protection provided by Office 365. Instead, it adds additional detection measures to block spam, malware, phishing, and zero-day attacks.
Alternatively, you can pay for the more expensive Microsoft Defender.
Why is outbound scanning necessary if I scan inbound emails?
Email account credentials can be obtained through phishing, brute force tactics, or stolen credentials. When an email account is compromised, it is common for the account to be used to send phishing emails from your domain. Outbound scanning detects malicious emails sent from a compromised account. Outbound scanning from advanced spam servers, like SpamTitan, also protects against data loss using data leak prevention technology (DLP).
Can I apply different spam filtering settings for each department?
Most spam filters allow you to apply spam filtering controls at three levels: Organization-wide, per department/user group, and individual user level. These controls are easy to apply if a spam filtering solution integrates directory services such as LDAP and AD.
How can I stop genuine emails from being blocked?
Most spam filters have low false positive rates and rarely block genuine emails. The use of machine learning mechanisms by advanced spam filters, like SpamTitan, improves the accuracy of a spam filter server over time. The easiest way to ensure genuine emails are not misclassified is to add trusted senders to an allowlist. Emails from a particular address or domain will then always be delivered.
What are layered phishing defenses?
Layered defenses used to detect and prevent spam are the best way to catch existing and emerging threats. Multiple unified layers of protection work by augmenting each other; if one mechanism fails to detect a malicious message, others are in place to ensure you are protected. An example would be the standard Office 365 spam filter, EOP. You add advanced spam and phishing detection by layering SpamTitan on top of EOP. Other layers that improve your email security posture include using a web filter and security awareness training to help employees recognize email threats.


