titanadmin - Page 7
by titanadmin | Mar 11, 2020 | Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
Microsoft has announced it has taken control of the U.S. infrastructure of the Necurs botnet and has taken steps to prevent the botnet operators from registering new domains and the rebuilding the Necurs infrastructure.
The Scale of the Necurs Botnet
The Necurs botnet first appeared in 2012 and has grown into one of the largest spam and malware distribution networks. The botnet consists of around 9 million devices that have been infected with Necurs malware. Each device within the botnet is under the control of the cybercrime group behind the botnet.
The Necurs botnet is used to commit a wide range of cybercrimes by the operators of the botnet as well as other cybercriminal groups who rent out parts of the botnet as a service. The Necurs botnet was used for malware and ransomware distribution, cryptocurrency mining, and attacks on other computers to steal credentials and confidential data. The Necurs botnet also has a distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) module capable of performing massive DDoS attacks, although this function is yet to be used.
The main use of the botnet is spamming. The botnet has been used to send vast quantities of spam email, including emails pushing fake pharmaceutical products, pump and dump stock scams, and Russian dating scams. To give an example of the scale of the spamming, over a 58-day period of observation, Microsoft found that a single Necurs malware-infected computer had sent out 3.8 million spam emails to 40.6 million email accounts. That is just one infected device out of 9 million! In 2017, the botnet was being used to spread Dridex and Locky ransomware at a rate of around 5 million emails an hour and between 2016 and 2019 the botnet was responsible for 90% of email-based malware attacks.
The Takedown of Necurs Infrastructure
Microsoft has tracked the criminal activity of the Necurs botnet operators for 8 years. The gang is believed to be Evil Corp, the Russian cybercriminal group behind the Dridex banking Trojan. Evil Corp has been named the most harmful cybercrime group in the world.
The takedown of the Necurs botnet involved a coordinated effort by Microsoft and partners in 35 countries. Microsoft obtained an order from the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York on March 5, 2020 to seize the U.S. domains used by the botnet operators. These domains were used to issue commands to the 9 million infected computers.
Simply seizing the domains would not be sufficient to take down the botnet, as the botnet’s command and controls servers could be rapidly rebuilt. Domains used by the threat actors are often taken down, so new domains are constantly registered weeks or months in advance.
The key to long-term disruption of the botnet was cracking the algorithm used by the threat actors to generate new domains. Microsoft analyzed the algorithm and calculated more than 6 million domains that would be used by the threat actors over the next 25 months. Steps have been taken to prevent those domains from being registered and becoming part of the Necurs infrastructure.
The 9 million devices around the world are still infected with Necurs malware. Microsoft and its partners have identified the infected devices and are working with ISPs and CERT teams around the world to rid those devices of the malware.
by titanadmin | Feb 17, 2020 | Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
Just a few days after new figures from the FBI confirmed business email compromise scams were the biggest cause of losses to cybercrime, news broke of a massive cyberattack on a Puerto Rico government agency. Cybercriminals had gained access to the email account of an employee, understood to work in the Puerto Rico Employee Retirement System.
The compromised email account was used to send requests to other government agencies requesting changes be made to standard bank accounts for remittance payments. Since the email account used was trusted, the changes to bank accounts were made. Scheduled payments were then made as normal and millions of dollars of remittance payments were wired to attacker-controlled bank accounts.
The Puerto Rico Industrial Development Company, a state-owned corporation that drives economic development of the country, was one of the worst hit. Emails were received requesting changes to bank accounts and two payments were made. The first payment of $63,000 was made in December and another payment of $2.6 million in January. Other departments were also targeted, including the Tourism Company. The latter made a payment of $1.5 million. In total, the scammers attempted to steal around $4.73 million.
The business email compromise scam was uncovered when those payments were not received by the correct recipients. Prompt action was then taken to block the transfers and some of the payments were frozen, but the government has not been able to recover around $2.6 million of the stolen funds.
A full investigation has been launched to determine how the attackers gained access to the email account to pull off the scam. While the method used has not been confirmed, BEC attacks usually start with a spear phishing email.
A phishing email is sent to a person of interest requesting urgent action be taken to address a problem. A link is supplied in the email that directs the user to a website that requests their email account credentials. The account can then be accessed by the attacker. Attackers often set up mail forwarders to receive a copy of every email sent to and from the account. This enables them to learn about the company and typical payments and construct highly convincing scam emails.
Once access to a corporate email account is gained, the BEC scam is much harder to identify and block. The best defense is to ensure that the initial phishing emails are not delivered, and that is an area where TitanHQ can help.
by titanadmin | Feb 17, 2020 | Phishing & Email Spam
A new report from the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has revealed the extent to which phishing is used to attack businesses and the huge losses that have resulted from another form of email attack – business email compromise (BEC) scams.
In 2019, IC3 received 467,361 complaints about cybercrime and there were reported losses in excess of $3.5 billion, up from $2.7 billion in 2018. The true losses and number of attacks will be far higher, as not all crimes and losses are reported. Phishing, vishing, smishing, and pharming attacks were the most prevalent crime types with 114,702 complaints submitted to IC3 in 2019. Those attacks resulted in losses of more than $57 million.
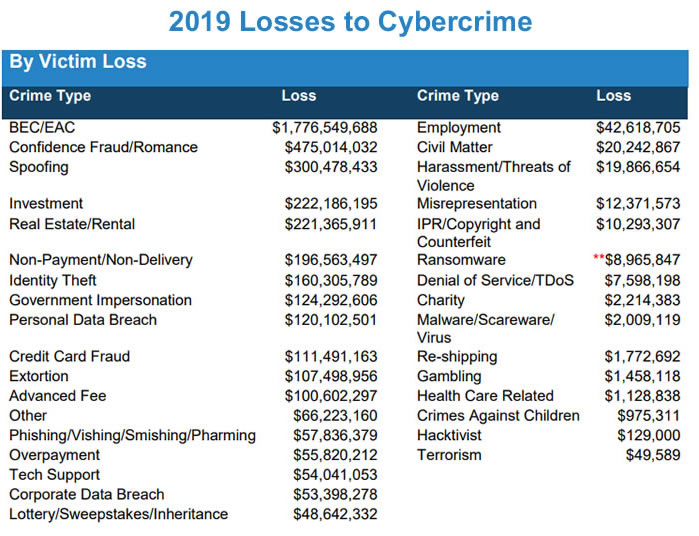
Source: IC3
There were 23,775 complaints about BEC attacks and losses to those attacks were more than $1.776 billion. On average, BEC attacks result in losses of around $75,000 and the attacks accounted for 50.75% of all losses to cybercrime in 2019.
Business email compromise attacks involve the impersonation of a known individual or company and a fake invoice and fraudulent wire transfer request. Alternatively, changes to vendor’s bank account details or requested or changes to direct deposit accounts for payroll. These email impersonation attacks involve spoofing an email account or compromising an account, with the latter usually achieved with phishing emails.
Email is also used to deliver ransomware – 2,0417 incidents and $8,965,847 in losses – and malware and viruses – 2,373 incidents and $2,009,119 in losses.
The Importance of a Layered Approach to Email Security
As the IC3 2019 cost of cybercrime report shows, the most common attack vector is email, so how can business owners protect against email-based attacks?
Businesses can either purchase cybersecurity solutions directly or engage a managed service provider to look after cybersecurity. If the decision is taken to manage cybersecurity in-house, it is essential to adopt a defense in-depth strategy and implement multiple layers of protection. Should one cybersecurity solution fail to block a threat, other layers will prevent the attack from succeeding.
Many businesses have adopted Office 365 and use it for email. Microsoft includes a basic level of email protection for Office 365 as standard – Exchange Online Protection (EOP). EOP serves as the first layer of protection against phishing attacks, malware, and spam, but EOP alone is not enough to block sophisticated phishing attacks, BEC attacks, and zero-day malware threats. An additional layer of protection is required.
Advanced Protection Against Phishing and Business Email Compromise Attacks
TitanHQ has developed an advanced anti-spam solution – SpamTitan – that provides an additional layer of protection against email threats.
To protect against known malware threats, dual anti-virus engines are used. However, new malware variants are constantly being released. Before AV engines can block these new threats, the threat must be identified and the malware signature is then added to the AV engine’s virus definitions. Until that happens, threats will not be identified as malicious and will be delivered to inboxes.
To improve protection against zero-day threats, TitanHQ uses sandboxing fro email. When a suspicious or unknown email attachment is received, it is sent to the sandbox where it is subjected to in-depth analysis to identify command and control center callbacks and potentially malicious actions.
Office 365 accounts are targeted by cybercriminals and their new phishing campaigns are tested against Office 365 protections to make sure the emails are delivered. One previous study showed that 25% of phishing emails are delivered to Office 365 inboxes.
To ensure phishing threats are detected that would otherwise not be blocked by EOP, SpamTitan uses a range of advanced detection techniques. They include multiple real-time blackhole lists and threat intelligence feeds, multi-layered message analysis, SURBL’s, Bayesian analysis, greylisting, and more. Protection against email impersonation attacks and spoofing is provided through Sender Policy Framework and DMARC, and all outbound emails are scanned to identify potential email account compromises.
SpamTitan is a full-service email security solution that protects your business, your employees, and your clients from email-based attacks. With SpamTitan, you can adopt a layered approach to email security at a very low cost per user.
If you want to make sure that your business is protected from costly email-based attacks, give the TitanHQ team a call.
by titanadmin | Feb 12, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
Emotet is the biggest malware threat faced by businesses and activity has increased considerably in recent weeks after a lull in December. Several new campaigns are now being identified each week, most of which are target businesses. One of the most recent campaigns uses a tried and tested technique to install the |Emotet Trojan. Malicious Word documents masquerading as invoices, estimates, renewals, and bank details.
The campaign mostly targets organizations in the United States and the United Kingdom, although attacks have also been detected in India, Spain, and the Philippines. Approximately 90% of emails in this campaign target financial services, with around 8% of attacks on companies in the food and drink industry.
The malicious Word documents are either attached to emails or hyperlinks are included in the emails that direct the user to a compromised website where the Word document is downloaded. The websites used are frequently changed and new Emotet variants are frequently released to prevent detection. Email security solutions that rely on AV engines to detect malware are unlikely to detect these zero-day threats as malicious.
Since Emotet is a massive botnet, emails spreading the Emotet Trojan come from many different sources. Email security solutions that rely on real-time blacklists are unlikely to detect these sources as malicious.
Emotet is primarily distributed via email from infected devices, but recently another distribution method has been identified. Emotet also spreads via Wi-Fi networks. This method has been used for almost two years, but it has only just been detected by security researchers at Binary Defense.
When Emotet is installed, a worm.exe binary is dropped that runs automatically. It attempts to connect to nearly Wi-Fi networks and brute forces weak passwords. Once connected to a Wi-Fi network, a search is conducted for non-hidden shares on the network. An attempt is made to enumerate all users connected to the Wi-Fi network, devices are brute forced, and the Emotet binary is dropped.
How to Block Emotet
The constantly changing tactics of the Emotet gang make detection difficult and no single solution will provide protection against all forms of attack. What is needed is a defense in-depth approach and layered defenses.
The primary defense against a predominantly email-based threat such as Emotet is an advanced spam filtering solution. Many businesses have used Office 365 and rely on the protection provided by Exchange Online Protection (EOP), which is included as standard with Office 365 licenses. However, EOP alone will not provide enough protection against Emotet. EOP will block all known malware threats, but it struggles to identify zero-day attacks. To block zero-day attacks, more advanced detection methods are required.
SpamTitan has been developed to work seamlessly with EOP to protect Office 365 email from zero-day threats. SpamTitan uses a variety of techniques to identify Emotet, including dual antivirus engines to block known Emotet variants and sandboxing to block zero-day attacks. Suspicious or unknown attachments are sent to the sandbox where they are subjected to in-depth analysis to identify command and control server callbacks and other malicious actions. SpamTitan also scans outgoing emails to identify attempts to spread Emotet from an already-infected machine. SpamTitan also incorporates DMARC to identify email impersonation and domain spoofing, which are commonly used in emails spreading Emotet.
To provide protection against the web-based element of attacks, including Emotet emails that use malicious hyperlinks rather than email attachments, another layer needs to be added to cybersecurity defenses – a DNS filtering solution such as WebTitan.
WebTitan uses real-time URL threat detection powered by 650 million end users. The real-time database includes more than 3 million malicious URLs and IP addresses and each day around 100,000 new malicious URLs are detected and blocked. WebTitan also includes real-time categorization and detection of malicious domains, full-path URLs, and IPs, with up-to-the-minute updates performed to block new malicious sources. As soon as a URL is identified as being used to distribute Emotet (or other malware) it is blocked by WebTitan. WebTitan also conducts link & content analysis, static, heuristic, & behavior anomaly analysis, and features in-house and 3rd party tools and feeds to keep users protected from web-based threats.
Other essential steps to take to tackle the threat from Emotet include:
- Disable macros across the organization
- Ensure operating systems are kept up to date and vulnerabilities are promptly patched.
- Set strong passwords to thwart brute force attacks
- Ensure endpoint protection solutions are deployed on all devices
- Provide security awareness training to employees
- Conduct phishing simulation exercises to identify employees that require further training
by titanadmin | Feb 10, 2020 | Internet Security, Network Security
The first California Consumer Privacy Act lawsuit has been filed over an alleged failure to adequately protect consumer data. The lawsuit has been filed against Hanna Andersson, a children’s clothing company, and its ecommerce platform provider, Salesforce.com.
The California Consumer Privacy Act took effect on January 1, 2020. Under Civil Code 1798.100 – 1798.199, consumers could start exercising their new rights under CCPA from the compliance date. One of those rights is being able to take legal action against companies for privacy violations, such as the theft of personal data in a data breach.
The California Consumer Privacy Act lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California on behalf of a victim of a 2019 data breach. The lawsuit alleges negligence and a failure to implement reasonable safeguards to protect consumer data, and that the data breach occurred as a direct result of the alleged negligence. A claim for damages has not been stated, although the right has been reserved to seek damages and relief at a later date.
The breach in question was announced by Hanna Andersson on January 15, 2020. Hackers had gained access to its systems and downloaded malware, which allowed the attackers to steal information such as names, personal information, and payment card data. That information was subsequently listed for sale on the dark web.
The California Consumer Privacy Act allows Californians to file for damages of up to $750 per data breach, so a class action California Consumer Privacy Act lawsuit arising from a sizeable data breach could prove extremely costly for a company. In this case, the data breach affected approximately 10,000 California residents, so damages up to $7,500,000 could potentially be claimed.
Enforcement of CCPA
Enforcement of compliance by the California Attorney General has been delayed and will start 6 months after the publication of the final regulations or July 1, 2020, whichever comes sooner. Since the final regulations have yet to be published, the enforcement date will be July 1, 2020. California Attorney General Xavier Bercerra has already stated that he will make an example of businesses that fail to comply with CCPA.
It should be noted that there is nothing in CCPA that prevents the state attorney general from issuing notices of noncompliance before that date and consumers can already file lawsuits to claim damages. It is therefore essential for all entities covered by CCPA to ensure that they are honoring the new consumer rights and have implemented safeguards to protect consumer data.
How TitanHQ Can Help with CCPA Compliance
TitanHQ offers two powerful security solutions that can help covered entities ensure the data of consumers is protected and data breaches are prevented. These two cybersecurity solutions protect against the two most common attack vectors – Email and the internet.
SpamTitan is a powerful anti-spam, anti-malware, and anti-phishing solution that protects email systems from phishing and spear phishing attacks, known and zero-day malware threats, and email-based ransomware attacks.
WebTitan is a companion solution that blocks the web-based element of phishing attacks, exploit kits, and drive-by malware downloads over the internet, while also controlling the content that employees can access on wired and wireless networks.
TitanHQ can also help covered entities comply with the right to know and right to delete consumer rights afforded by CCPA through ArcTitan. ArcTitan is an email archiving solution that allows organizations to meet state and federal email data retention requirements and quickly find emails containing consumer data. If a California resident exercises their right to know what data is held on them by a company, or requests all of their personal data is deleted, that information can quickly be found in the archive. ArcTitan will also allow you to quickly find email data for eDiscovery in the event of any legal disputes.
For further information on these solutions, to schedule a product demonstration, or to arrange a free trial of the full solutions (with full customer support), give the TitanHQ team a call today.
by titanadmin | Feb 5, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Software
Tax season is now underway and business email compromise scammers have stepped up their efforts to obtain W-2 forms for tax fraud. These attacks often start with spear phishing emails targeting the CEO and the executive board. Once email credentials have been obtained, the accounts are then accessed, and emails are sent internally to payroll and the HR department requesting the W-2 forms of employees who have worked in the previous tax year.
Scammers target businesses as there is much greater potential for profit than attacks on individual taxpayers, although consumers also need to be wary of IRS-related phishing scams. This time of year sees an increase in IRS phishing scams. Scammers impersonate the IRS and send emails informing taxpayers about a tax refund that is due and demands are sent for outstanding tax, with threats of dire consequences if prompt action is not taken to address issues.
Advances in email security have meant cybercriminals have had to get creative as it is harder to sneak phishing emails past email defenses. Phishing scams are now commonly initiated via text message, post, and over the telephone. There has already been one campaign identified where consumers are being targeted using robocalls warning that Social Security numbers have been suspended after suspicious activity was detected.
While many of these scams seek personal information, others are conducted to spread malware. One threat group that started its tax-related scams early this year is the Emotet gang. A campaign is currently being conducted that uses emails containing fake signed W-9 forms.
Signed W-9 forms are requested by companies from their contractors if they have been paid in excess of $600 during the tax year. Many companies will have requested signed W-9 forms from their contractors to confirm addresses and tax identification numbers, so they will be expecting copies of these forms in their inboxes.
The Emotet emails are short and to the point, saying “Thank you for your help. Pleased see attached file.” The emails include a Word document attachment named W-9.doc. When the document is opened, the Office 365 logo is displayed along with text stating the document was created in OpenOffice and requires the user to enable editing and enable content. Doing so triggers the silent download of the Emotet Trojan.
This is just one of the tax-related messages being used by the Emotet gang. There are likely to be many more variants sent over the next few weeks. Other cybercriminal gangs will similarly be conducting their own tax-themed phishing campaigns to spread different malware variants and ransomware.
Businesses, tax preparers, and consumers need to be on high alert during tax season for phishing scams and emails spreading malware.
Now is a good time for businesses to review their cybersecurity defenses and enhance protection against phishing and malware attacks. If you use Office 365 and rely on the anti-phishing protections built into Office 365 (EOP), you should consider enhancing your anti-phishing and anti-malware protection with a third-party spam filter – One that has superior malspam detection capabilities.
This is an area where TitanHQ can help. SpamTitan uses a variety of advanced techniques to detect and block phishing threats and zero-day malware, including an email sandbox where unknown and suspicious email attachments are subject to in-depth analysis. Give the TitanHQ team a call to find out more about SpamTitan, improving Office 365 malware and phishing protection, and to arrange a product demonstration and free trial of SpamTitan.
In the meantime, take steps to alert your workforce about tax-season phishing scams and prepare them in case a phishing email arrives in their inbox. An email alert sent to your employees about the threat of tax-season scams could prevent a costly phishing attack or malware infection.
by titanadmin | Jan 31, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
A novel coronavirus phishing campaign has been detected that uses scare tactics to trick users into infecting their computer with malware.
The World Health Organization has now declared the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak a global emergency. The number of cases has increased 10-fold in the past week with almost 9,100 cases confirmed in China and 130 elsewhere around the world.
A worldwide health crisis such as this has naturally seen huge coverage in the press, so it is no surprise that cybercriminals are capitalizing on the concern and are using it as a lure in a malspam campaign to scare people into opening an email attachment and enabling the content.
A novel coronavirus phishing campaign has been detected that uses a fake report about the coronavirus to get email recipients to open a document that details steps that should be taken to prevent infection. Ironically, taking the actions detailed in the email will actually guarantee infection with a virus of a different type: Emotet.
The coronavirus phishing campaign was identified by IBM X-Force researchers. The campaign is targeted on users in in different Japanese prefectures and warning of an increase in the number of local confirmed coronavirus cases. The emails include a Word document attachment containing the notification along with preventative measures that need to be taken.
If the attachment is opened, users are told they must enable content to read the document. Enabling the content will start the infection process that will see the Emotet Trojan downloaded. Emotet is also a downloader of other malware variants. Other banking Trojans and ransomware may also be downloaded. Emotet can also send copies of itself to the victim’s contacts. Those messages may also be coronavirus related.
To add credibility, the Emotet gang makes the emails appear to have been sent by a disability welfare service provider in Japan. Some of the captured messages include the correct address in the footer.
More than 2,000 new infections have been confirmed in the past 24 hours in China and all of its provinces have now been impacted. Cases have now been reported in 18 other countries with Thailand and Japan the worst hit outside of China with 14 cases confirmed in each country. As the coronavirus spreads further and more cases are reported, it is likely that the Emotet gang will expand this campaign and start targeting different countries using emails in different languages. Kaspersky lab has also said that it has identified malspam campaigns with coronavirus themes that use a variety of email attachments to install malware.
Businesses can protect against Emotet, one of the most dangerous malware variants currently in use, by implementing a spam filtering solution such as SpamTitan that incorporates a sandbox where malicious documents can be analyzed in safety to check for malicious actions.
For further information on protecting your email system, contact TitanHQ today.
by titanadmin | Jan 30, 2020 | Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
It has been well documented how much time businesses waste dealing with spam and there is no denying the threat that malicious spam emails (malspam) pose, but it is not just a problem for big business. Spam in academia is also a major problem.
A recent study published in the journal, Scientometrics, explores the cost of spam in academia. The study was primarily focused on spam emails sent by new, non-peer-reviewed journals that are attempting to gain a share of the market. These journals are adopting the same spam tactics often used by scammers to sell cheap watches and cut-price medications and for phishing and spreading malware.
Three researchers – Jaime A. Teixeira da Silva, Aceil Al-Khatib, and Panagiotis Tsigaria – attempted to quantify the amount of time that is being wasted dealing with those messages and the losses that result.
To assess the extent of the problem, the researchers used figures from several studies on spamming to obtain an average number of targeted spam emails that academics receive each day. They opted for a conservative figure of 4-5 messages, per academic, per day. Most of those messages take just a few seconds to open and read but that time mounts up. They assumed an average time of 5 seconds per message – less than half a minute per day. That equates to $100 per researcher, per year at an average hourly rate of $50. Using the United Nations estimate of the number of researchers in academia globally, the total global cost of spam in academia was estimated to be $1.1 billion a year.
That figure is based on the lost time alone and does not factor in non-targeted spam emails – bulk unsolicited emails not specifically targeting researchers. Add in the time dealing with those messages and the global cost reaches $2.6 billion a year. To put the cost into perspective, $2.6 million is much more than the time researchers devote to peer review, which has been estimated at a cost of $1.9 billion a year. The figures do not include the considerable losses due to phishing, malware, and ransomware attacks. Factor in those costs and the losses would be several orders of magnitude higher.
Co-author of the study, Panagiotis Tsigaris, a professor of economics at Thompson Rivers University in Canada, explained that there is no silver bullet when it comes to dealing with spam and suggested several ways that the cost of spam in academia could be reduced.
Tsigaris suggests that penalties should be increased for publishing in predatory journals, and that academics should be educated about spam email and that improvements should be made to email filtering technology.
Here at TitanHQ, we are well aware of the problem of spam, both in terms of the productivity losses that spam causes, and harm caused by malicious spam emails.
To help prevent losses and downtime due to spam and email-based threats, TitanHQ has developed a powerful, easy-to-use, and cost-effective cloud-based spam filtering solution called SpamTitan. SpamTitan has been independently tested and shown to block in excess of 99.9% of spam email, 100% of known malware and ransomware threats, and thanks to a host of detection measures and sandboxing, SpamTitan is also effective at blocking zero-day (new) malware and ransomware threats.
To find out more about SpamTitan and how you can block more spam and ensure malicious emails do not reach your researchers’ inboxes, give the TitanHQ team a call today.
by titanadmin | Jan 22, 2020 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Website Filtering
 TitanHQ has announced a new partnership with Pax8. The partnership means Pax8 partners now have access to TitanHQ’s cloud-based email security solution – SpamTitan – and its DNS filtering solution, WebTitan.
TitanHQ has announced a new partnership with Pax8. The partnership means Pax8 partners now have access to TitanHQ’s cloud-based email security solution – SpamTitan – and its DNS filtering solution, WebTitan.
Pax8 is the leader in cloud distribution. The company simplifies the cloud buying process and empowers businesses to achieve more with the cloud. The company has been named Best in Show for two consecutive years at the Next Gen and XChange conferences and is positioned at number 60 in the 2019 Inc. 5000 list of the fastest growing companies.
Pax8 carefully selects the vendors it works with and only offers market-leading channel friendly solutions to its partners. When searching for further cybersecurity solutions for its partners, TitanHQ was determined to be the perfect fit. TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email and web security solutions for managed service providers (MSPs) serving the SMB marketplace and its cybersecurity solutions are much loved by users. This was clearly shown in the 2019 G2 Crowd Report on Email Security Gateways where SpamTitan was named leader, having achieved 4- or 5-star ratings by 97% of its users, with 92% saying they would recommend the solution to other businesses.
Phishing, malware, and ransomware attacks have all increased in the past year and the cost of mitigating those attacks continues to rise. By implementing SpamTitan and WebTitan, SMBs and MSPs can secure their email environments and block web-based threats and keep their networks secure.
SpamTitan provides excellent protection for Office 365 environments. The solution detects and blocks phishing and email impersonation attacks and prevents known and zero-day malware and ransomware threats from reaching inboxes. The WebTitan Cloud DNS filtering solution blocks the web-based component of cyberattacks by preventing end users from visiting malicious websites, such as those harboring malware and phishing kits.
Both solutions are quick and easy to implement, can be seamlessly integrated into MSPs service stacks and cloud-management platforms, and Pax8 partners benefit from highly competitive and transparent pricing, centralized billing, and leading customer support.
“I am delighted to partner with the Pax8 team,” said Ronan Kavanagh, CEO, TitanHQ. “Their focus and dedication to the MSP community are completely aligned with ours at TitanHQ, and we look forward to delivering our integrated solutions to their partners and customers.”
by titanadmin | Jan 21, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
The Emotet botnet took a Christmas holiday but it’s now up and running again and the massive phishing and spamming campaigns have resumed. These campaigns, which involve millions of spam emails, use a variety of lures to trick people into opening an attachment and enabling content. The content in question includes a macro that runs a PowerShell command that downloads and executes the Emotet Trojan.
The Emotet Trojan is bad news. Emotet was once just a banking Trojan whose purpose was to steal online banking credentials. It still does that and much more besides. Emotet also steals credentials from installed applications and browsers. It is also self-propagating and will send copies of itself via email to the victim’s contacts. As if that was not bad enough, Emotet has another trick up its sleeve. It is also a downloader of other malware variants such as the TrickBot Trojan and Ryuk ransomware. These additional payloads allow data to be stolen and sold for profit and for files across the network to be encrypted and ransom demands issued. Emotet has also delivered cryptocurrency miners in the past and could deliver any number of other malware payloads.
The scale of the botnet is staggering. In the first quarter of 2019, Emotet was responsible for 6 out of 10 malicious payloads delivered via email. There are often breaks in activity, but even though the threat actors behind the botnet took almost half of 2019 off, Emotet still ranks as the top malware threat of the year.
Emotet sprung back to life on January 13, 2020, with targeted attacks on the pharmaceutical industry in North America, but it didn’t take long for the attacks to spread even further afield. Now more than 80 countries are being attacked and in addition to English, campaigns have been detected in Italian, Polish, German, Spanish, Japanese, and Chinese.
The lures used to fool end users into opening email attachments are highly varied and often change. Tried and tested lures such as fake invoices, orders, statements, agreements, payment remittance notices, receipts, and delivery notifications are often used in attacks on businesses, which are the primary targets. Before the botnet shut down for a break in December, Greta Thunberg-themed emails were being used along with Christmas party invitations. A host of new lures can be expected in 2020.
The themes of the emails may change but the messages have one thing in common. They require an end user to take action. That is usually opening a document, spreadsheet, or other file, but could be a click on a hyperlink in an email. Once that action is taken, Emotet will be silently downloaded.
There are two main ways of blocking attacks and both are necessary. The first is to ensure that the email system is secure, which means implementing an effective spam filter. Businesses that use Office 365 will have a modicum of protection through Exchange Online Protection (EOP), which is included with Office 365 subscriptions. However, businesses should not rely on EOP alone. Layered defenses are required.
SpamTitan is a powerful spam filter that will improve protection against malware threats such as Emotet. SpamTitan can be layered on top of Office 365 to provide greater protection and prevent the malware from being delivered to inboxes. Dual anti-virus engines are incorporated into the solution to detect known threats and SpamTitan includes a sandbox for identifying threats that signature-based detection mechanisms miss.
Many businesses deploy a variety of security solutions but fail to prepare their employees for an attack. If malicious emails make it past security solutions and are delivered to inboxes, all it takes is for one employee to fail to spot the threat and respond for Emotet to be installed (and potentially ransomware as well). It is therefore important to provide regular security awareness training to everyone in the company from the CEO down. If employees are not told how to identify malicious emails, they cannot be expected to spot threats and report the messages to the security team.
Fortunately, through a combination of email security solutions and security awareness training, the threat from Emotet can be neutralized. For more information on the former, give TitanHQ a call today.
by titanadmin | Jan 20, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
Whenever there is a major event that attracts a lot of media attention cybercriminals will be poised to take advantage, so it is no surprise that warnings are being issued about Travelex phishing scams.
The Travelex ransomware attack that struck on New Year’s Eve involved a ransomware variant called Sodinokibi. The gang responsible is one of the most prolific threat groups using ransomware. The group’s attacks are highly targeted and seek to encrypt entire networks and the ransom demands reflect the scale of encryption. Travelex was initially issued with a demand for a payment of $3 million. That soon doubled to $6 million when payment was not made within the allocated timescale.
The fallout from the attack has been immense, which is unsurprising given that Travelex is the largest provider of currency exchange services worldwide. Many banks and retailers rely on Travelex to provide for their currency exchange services. Without access to those online services, currency exchange services came to a grinding halt. It has taken two weeks for Travelex to start bringing some of its services back online, but its website remains down and the disruption continues.
The attackers claimed to have stolen large quantities of customer data from Travelex. The attackers threatened to publish or sell the data if the ransom was not paid. This tactic is becoming increasingly common with ransomware gangs. In this case, the sodinokibi gang claimed to have gained access to Travelex systems 6 months previously and said they had stolen customer data including names, payment card information, and Social Security numbers and National Insurance numbers. The gang had also recently attacked the American IT company Artech Systems and had posted 337MB of data stolen in that attack, demonstrating to others that it was not an empty threat. Travelex maintained that no customer data had been stolen, but that has yet to be confirmed.
Warning Issued About Travelex Phishing Scams
Travelex customers should naturally err on the side of caution and monitor their accounts for signs of fraudulent use of their information but there are other risks from an attack such as this.
Travelex has issued a warning to its customers recommending they should be alert to the threat of phishing attacks via email and over the phone. Opportunistic scammers often take advantage of major events such as this and Travelex phishing scams are to be expected, as was the case following the TalkTalk data breach. These phishing scams are likely to be most effective on Travelex customers who have lost money as a result of the attack. Any offer of compensation or a refund is likely to attract a response.
For consumers, the advice is never to open email attachments or click on links in unsolicited emails. Businesses should also take steps to protect their networks from malware and phishing attacks.
Businesses should adopt a defense in depth strategy to protect against phishing scams and malware attacks. An advanced email security solution such as SpamTitan should be used to protect Office 365 accounts. SpamTitan improves protection against zero-day malware and phishing threats and blocks threats at the gateway.
A web filtering solution such as WebTitan should be used to block the web-based component of phishing and malspam campaigns and prevent end users from visiting malicious websites. End user training is also a must. It is important to teach employees how to identify phishing emails and malspam, and condition them how to respond when suspicious emails are received.
by titanadmin | Jan 16, 2020 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
A new ransomware threat – Ako ransomware – has emerged which is targeting business networks and is being distributed via spam email. The ransomware is being offered to affiliates under the ransomware-as-a-service model and the aim of the attackers is clear. To maximize the probability of payment of the ransom by making recovery harder, and to steal data prior to encryption to ensure the attack is still profitable if the ransom is not paid. Having the data could also help convince the victims to pay up, as we have seen in recent attacks involving Maze and Sodinokibi ransomware, where threats are issued to publish stolen data if the ransom is not paid.
The developers of Ako ransomware appear to be going for large ransom payments, as they are not targeting individual workstations, rather the entire network. The ransomware scans local networks for other devices and will encrypt network shares. The ransomware deletes shadow copies and recent backups and disables Windows recovery to make recovery more difficult without paying the ransom.
Encrypted files are given a randomly generated file extension and retain the original file name. No ransom amount is stated in the ransom note. Victims are required to contact the attackers to find out how much they will need to pay for the keys to decrypt their files.
One of the intercepted emails being used to distribute the ransomware uses a password-protected zip file as an attachment. The email appears to be a business agreement which the recipient is asked to check. The password to open and extract the file is included in the message body. The zip file attachment – named agreement.zip – contains an executable file which will install Ako ransomware if it is run. The malicious file is called agreement.scr.
There is no free decryptor for Ako ransomware. Recovery without paying the ransom will depend on whether viable backups exist that have not also been encrypted. It is therefore important to make sure backups are regularly performed and at least one copy of the backup is stored on a non-networked device to prevent it also being encrypted by the ransomware. Backups should also be tested to make sure file recovery is possible.
Since Ako ransomware is being distributed via spam email, this gives businesses an opportunity to block an attack. An advanced spam filtering solution should be implemented that scans all inbound messages using a variety of detection mechanisms to identify malware and ransomware threats. A sandbox is an important feature as this will allow email attachments to be analyzed for malicious activity. This feature will improve detection rates of zero-day threats.
nd user training is important to ensure that employees do not open potentially malicious files. Training should condition employees never to open email attachments in unsolicited emails from unknown senders. As this campaign shows, any password protected file sent in an unsolicited email is a big red flag. This is a common way that ransomware and malware is delivered to avoid detection by antivirus solutions and spam filters.
Anti-spam solutions and antivirus software will not be able to detect the threat directly if malicious files are sent in password-protected archives, which can only be opened if the password is entered. Rules should therefore be set to quarantine password-protected files, which should only be released after they have been manually checked by an administrator. With SpamTitan, these rules are easy to set.
Ako ransomware is one of many new ransomware threats that have been released in recent months. High profile attacks on companies such as Travelex that see massive ransom demands issued, which in many cases are paid, show a huge payday is possible.
Ransomware developers will keep developing new threats for as long as attacks remain profitable, and there is not likely to be a shortage of affiliates willing to run spamming campaigns to get their slice of the ransom payments.
With the attacks increasing, it is essential for you to have strong defenses that can detect and block malware, ransomware, and phishing threats, and that is an area where TitanHQ can help.
To find out more about how you can improve your defenses against email and web-based threats, give the TitanHQ team a call today.
by titanadmin | Jan 15, 2020 | Network Security
The Travelex ransomware attack that started around December 31, 2019 is one of several recent ransomware attacks where threat actors have upped the ante by threatening to publish data stolen from victims prior to the deployment of ransomware.
A New Trend in Ransomware Attacks
Most ransomware attacks, especially those conducted by affiliates using ransomware-as-a-service, see ransomware deployed instantly. An employee receives a ransomware attachment via email, opens the attachment, and the encryption process is started. Now, several threat actors have taken steps to increase the probability of their ransom demand being paid.
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has recently issued warnings about changing ransomware tactics, which now involve data theft prior to file encryption. This tactic is nothing new, as several threat actors have been conducting these types of attacks for some time, attacks of this nature have been increasing.
to the network is gained, the attackers then move laterally and gain access to as many devices as possible. Data is stolen and when the attackers have stolen as much as they want, ransomware is deployed. In these types of attacks, the time between the initial compromise and deployment of ransomware is typically several months.
Data may be stolen and sold online with the ransomware deployed as a coup de grace after a long-term compromise to extort money from the company. Now it is increasingly common for a threat to be issued along with the ransom demand that the stolen data will be published or sold if the ransom is not paid.
This tactic has been adopted by the threat actors behind Maze ransomware and they have gone ahead and published stolen data when the ransom was not paid. The threat actors using MegaCortex ransomware and LockerGoga ransomware have similarly issued threats.
Now the gang behind Sodinikibi (REvil) ransomware have also changed tactics and have started issuing threats to publish stolen data. The Sodinokibi gang have made several threats to sell on or publish stolen data but it was only recently that they did just that. The gang attacked Artech Information Systems, one of the largest IT staffing companies in the U.S. When the ransom demand was not paid, 337MB of stolen data was published on a Russian hacking and malware forum. The Travelex ransomware attack is one of the latest Sodinokibi ransomware attacks, and a threat to publish stolen data was similarly issued.
The Travelex Ransomware Attack
On New Year’s Eve, Travelex took its systems offline to contain the infection and limit the damage caused. More than two weeks on, Travelex systems are still offline although the company is now starting to restore some of its systems. The number of branches affected by the attack, and banks and other companies that rely on its currency exchange services, makes this one of the most serious and damaging ransomware attacks ever.
With its systems offline, Travelex has been unable to provide its currency services to banks such as HSBC, Royal Bank of Scotland, NatWest, First Direct, Barclays and Lloyds, all of which rely on Travelex for providing their currency services. Many other companies, such as the supermarket chains Sainsbury’s and Tesco, have also had to stop providing online currency services to their customers. Travelex has been forced to provide services manually using pen and paper for over the counter currency exchanges in its branches. More than 70 countries in which Travelex operates were affected by the attack.
Travelex has only released a limited amount of information about the attack, but the attackers have been in contact with several media outlets. Initial reports suggested a payment of $3 million was required for the keys to unlock the encryption, although the demand doubled to $6 million when payment was not received within the stipulated 2 days. The attackers also threatened to publish data stolen in the attack if the payment was not made within 7 days.
Travelex issued a statement saying no customer data was breached and that the infection was contained, a position that has been maintained since the attack, even though the Sodinokibi gang has threatened to publish customer data.
The Sodinokibi ransomware gang, through a spokesperson, said the gang had stolen 5GB of customer data including customers’ names, dates of birth, credit card information, Social Security numbers, and National Insurance numbers. The gang claimed that all stolen data would be deleted and would not be used if the ransom demand was paid, but that the data would be sold if payment was not received. The gang also said access to Travelex systems was gained 6 months before the ransomware was deployed.
How Was Travelex Attacked?
It is not known at this stage exactly how ransomware was installed on its network, but there have been several security researchers that have offered some clues. According to BleepingComputer, Travelex was using insecure services prior to the attack. Security researcher Kevin Beaumont found Travelex had AWS Windows servers that did not have Network Level Authentication enabled, which could have given the attackers the opportunity they needed to launch an attack.
A critical vulnerability in the Pulse Secure VPN enterprise solution for secure communications – CVE-2019-11510 – was identified and was patched by Pulse Secure on April 24, 2019, but many companies were slow to apply the patch, despite receiving multiple warnings from Pulse Secure. An exploit for the vulnerability was made public on August 21, 2019.
Troy Mursch, chief research officer at Bad Packets, found that Travelex had not applied the patch by the time the exploit was released. The Sodinokibi ransomware gang said they compromised Travelex 6 months prior to the deployment of ransomware. This could have been the vulnerability that was exploited.
Recovery Now Well Underway
On January 13, 2020, more than 2 weeks after the ransomware attack was experienced, Travelex issued a statement confirming that the recovery process was well underway, although the firm’s website was still offline. The company had started restoring its currency services to banks and its own network. Internal order processing has been restored and customer-facing systems are slowly being brought back online. What Travelex has not confirmed is whether the ransom was paid. No Travelex data appears to have been published online so it is possible that a ransom payment has been negotiated with the attackers.
Cost of the Travelex Ransomware Attack
The ransom payment is considerable but is likely to be several orders of magnitude less than the costs of downtime and disruption to its services.
No customer data appears to have been misused, but Travelex could still face a barrage of lawsuits from customers and the Information Commissioner’s Office and other data protection authorities my choose to fine Travelex over the data breach, either for the exposure of data or for the failure to report under GDPR.
GDPR requires data breaches to be reported to data protection authorities within 72 hours and it appears that did not happen. The maximum financial penalty for a GDPR violation is €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual turnover, whichever is greater. Travelex’s global annual turnover in 2018 was $947.86 million. A fine of $189.57 million could therefore be issued. It should be noted that even if data was not stolen by the attackers and was just made inaccessible, it still counts as a reportable data breach under GDPR.
A payment of $6 million to the attackers would only be a tiny proportion of the total losses from downtime, lost business, lawsuits, and regulatory fines.
by titanadmin | Dec 30, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
Customers of Canadian banks have been targeted by cybercriminals in an extensive phishing campaign that has been ongoing for at least the past two years, according to Check Point Research which uncovered the campaign. As with many other financial phishing scams, the attackers spoof the website of a well-known bank and create a virtual carbon copy of the home page of the bank on a lookalike domain, which often only differs from the genuine domain name by a letter or two.
A link to the fraudulent site is then sent in a mass spamming campaign to email addresses on the specific country top level domain where the bank operates. The emails instruct users to visit the banks website and login, usually under the guise of a security alert. When the link in the email is clicked, the user is directed to the spoofed site and may not notice the domain name is not quite right. They then enter their login credentials which are captured by the scammers. The credentials are then used to make fraudulent wire transfers to accounts controlled by the attackers.
In this campaign, the emails include a PDF email attachment. PDF files tend to be trusted to a higher degree than Word documents and spreadsheets, which end users have usually been instructed to treat as suspicious. The PDF file includes a hyperlink, which the user is instructed to click. Since the hyperlink is in the document rather than the email body, it is less likely to be scanned by email security solutions and has a higher chance of being delivered.
The user is told that they are required to update their digital certificate to continue using the online banking service. The PDF file includes the bank logo and a security code, which the user is required to enter when logging in. The code is included in the PDF attachment rather than email body for security reasons. As with most phishing scams, there is urgency. The recipient is told that the code expires in 2 days and that they must register within that time frame to avoid being locked out of their account.
The landing pages on the websites are identical to those used by the banks as the attackers have simply taken a screen shot of the bank’s landing page. Text boxes have been added where the username, password, and token number must be entered. Users are then asked to confirm the details they entered while the attackers attempt to access their account in real-time and make a fraudulent transfer.
These tactics are nothing new. Scams such as this are commonplace. What is surprising is how long the campaign has been running undetected. The scammers have been able to operate undetected by registering many lookalike domains which are used for a short period of time. Hundreds of different domains have been registered and used in the scam. At least 14 leading banks in Canada have had their login pages spoofed including TD Canada Trust, Scotiabank, Royal Bank of Canada, and BMO Bank of Montreal.
All of the websites used in the scam have now been taken down, but it is all but guaranteed that other lookalike domains will be registered and further scams will be conducted.
by titanadmin | Dec 27, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
A spamming campaign has been detected that is piggybacking on the popularity of Greta Thunberg and is using the climate change activist’s name to trick individuals into installing the Emotet Banking Trojan.
Emotet is one of the most active malware threats. Emotet was first detected in 2014 and was initially used to steal online banking credentials from Windows users by intercepting internet traffic. Over the years it has undergone several updates to add new functionality. It has had a malspam module added, which allows it to send copies of itself via email to a user’s contacts. Emotet also includes a malware downloader, allowing it to download a range of other malware variants such as other banking Trojans and ransomware.
The malware is used indiscriminately in attacks on individuals, businesses, and government agencies, with the latter two being the main targets. Emotet is primarily spread via spam email, and while exploits are not used to spread to other devices on the network – EternalBlue for instance – other malware variants downloaded by Emotet can. TrickBot for instance.
The Greta Thunberg spam campaign aims to get users to open a malicious Word attachment and enable content. If that happens, Emotet will be silently downloaded to the user’s device, sensitive banking information will be stolen, and further malware may be downloaded.
The campaign was active over the holiday period and used a variety of Christmas-themed lures to entice users into opening the email attachment. Some of the emails did not include an attachment and instead used a hyperlink to direct the user to a website where the malicious document could be downloaded.
One of the emails wished the recipient a Merry Christmas and urged them to consider the environment this Christmastime and join a demonstration in protest against the lack of action by governments to tackle the climate crisis. The email claimed details about the time and location of the protest were included in the Word document. The email also requested the recipient to send the email on to all their colleagues, friends, and relatives immediately to get their support as well. Several variations along that theme have been detected.
To increase the likelihood of the recipient enabling content, when opened the document displays a warning that appears to have been generated by Microsoft Office. The user is told that the document was created in OpenOffice and it is necessary to first enable editing first and then enable content. Doing the latter will enable macros which will start the infection process.
The emails are well written and have been crafted to get an emotional response, which increases the likelihood of the user taking the requested action. The emails have been sent in multiple languages in many different countries.
Whenever there is a major news event, popular sports tournament, or other event that attracts global interest, there will be cybercriminals taking advantage. Regardless of the theme of any email, if it is unsolicited and asks you to click a link or open an email attachment, it is best to assume that it is malicious.
Businesses can protect their networks against threats such as these by implementing an advanced spam filtering solution such as SpamTitan. SpamTitan will identify threats such as phishing attacks and will prevent the messages from reaching inboxes. SpamTitan also includes dual anti-virus engines to detect known malware and machine learning techniques and sandboxing to identify and block zero-day malware.
For further information on how SpamTitan can protect your business from email threats such as this, contact TitanHQ today.
by titanadmin | Dec 23, 2019 | Spam Advice, Spam Software
The majority of businesses have experienced a phishing attack in the past year, and according to one survey on SMBs in the United States, 72% have experienced a phishing attack in the past 3 months.
In healthcare, phishing is the leading cause of data breaches by some distance. In November 2019, there were 17 phishing-related data breaches reported to the Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights out of 33 for the month. Since OCR only makes breach reports public if they have resulted in the exposure of 500 or more records, the total number of phishing attacks is likely to be substantially higher.
Phishing attacks are increasing, and the reason is simple. Phishing is the easiest way of attacking an organization to deliver malware or obtain sensitive information. That is because phishing targets the weakest link: Employees. Employees are getting better at identifying phishing emails through security awareness training, but cybercriminals have responded and are now conducting highly sophisticated phishing attacks that are much harder for employees to identify.
There has also been an increase in spear phishing attacks. This is a much more targeted form of phishing. Instead of millions of emails being sent out in a campaign, only a handful are sent or to very specific targets. The emails are written to maximize the chances of success and are usually personalized.
So how can a business improve its defenses against phishing and spear phishing? Unfortunately, there is no silver bullet. Businesses need to take a defense in depth approach to significantly improve resilience to phishing attacks.
The best place to start is with an advanced email security solution. Phishing requires some form of manual action in order to succeed. If you prevent phishing emails from reaching inboxes, employees will not be able to click on links or download malware. An advanced email security solution will be able to block the vast majority of phishing emails before they reach your email system.
You will no doubt already have a spam filtering solution in place, but is it effective? Are phishing emails still being delivered? One common mistake made by SMBs is to believe that their Office 365 environment is well protected by default, when the reality is Exchange Online Protection (EOP) that comes with Office 365 fails to block many phishing attempts. One study showed 25% of phishing emails were not blocked by EOP. If you want to improve your defenses against phishing, you should use a third-party anti-spam and anti-phishing solution on top of EOP: One that compliments EOP but provides greater protection. SpamTitan for example.
With more phishing emails being blocked, your security posture will be much improved, but you can’t stop there. No anti-phishing solution will block all phishing threats, 100% of the time. Since all it takes is for one phishing email to be clicked for a data breach to occur, you need to add another layer to your defenses.
A DNS filtering solution provides protection against the web-based part of phishing attacks. When an employee clicks a link in an email and is directed to a fake Office 365 login page or a site where malware is downloaded, the attempt to access the site will be blocked.
A DNS filter blocks attempts to access phishing sites at the DNS lookup stage, before any web content is downloaded. If an attempt is made to access a phishing site, the employee will be directed to a block page before any harm is done. DNS filters can also block malware downloads from sites that are not yet known to be malicious.
Employees are the weak link that are targeted by cybercriminals so it is important they are trained how to recognize phishing emails. You should provide security awareness training regularly to develop security aware culture in your organization. Over time, employees can be conditioned to respond correctly and report phishing threats to the security team. Also conduct phishing simulation exercises to make sure training has been effective. A failed phishing simulation allows you to identify a weak link and provide further training.
If all of the above defenses have failed, there is another layer that can keep your business protected: Multi-factor authentication. MFA requires another factor to be used before access to an email account or other system is provided. If an employee’s login credentials are disclosed in a phishing attack, MFA should stop those credentials from being used by a cybercriminal to access to gain access email accounts and other systems.
All of these layers are necessary to block today’s sophisticated phishing threats. It may seem like a lot of expense, but the above anti-phishing measures need not be expensive. TitanHQ can’t train your employees to be security titans, but through SpamTitan Email Security and WebTitan DNS filtering, phishing threats can be blocked.
by titanadmin | Dec 17, 2019 | Internet Security, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Advice, Spam Software, Website Filtering
IT professionals have long known that employees are a weak link in the security chain. Recent studies have confirmed this to be the case. Employees are poor at identifying phishing emails and other email-based threats and, to be fair on employees, many have received no training and phishing scams are becoming much more targeted and sophisticated.
The number of successful phishing attacks on businesses is difficult to determine, as many attacks go unreported, even when they result in the exposure of consumer data. In regulated industries, such as the healthcare industry in the United States, the picture is much clearer.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act – or HIPAA as it is better known – requires healthcare organizations to report breaches of patient information. Summaries of data breaches of 500 or more records are also made public and can be seen on the Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights data breach portal.
In 2019 alone, there have been at least 147 incidents of hacking of email accounts. The cost of those breaches is staggering. In those 147 incidents, the hacked email accounts contained the records of 2,762,691 individuals. According to the Ponemon Institute/IBM Security 2019 Cost of a Healthcare Data Breach report, the cost per exposed healthcare record is $423. Those breaches are therefore likely to have cost $1,168,618,293.
A recent study conducted by GetApp confirmed how often employees are fooled by phishing attacks in other industries. For the study, 714 individuals were surveyed from a range of businesses in the United States. Almost a quarter of those businesses have experienced at least one successful phishing attack and 43% of employees said that someone in their organization had clicked on a phishing email.
The aim of the study was to explore whether businesses were providing security awareness training to their employees to help them identify phishing emails. Only 27% of organizations did. It is therefore no surprise that employees often fall for phishing scams.
The provision of security awareness training, with a particular focus on phishing and social engineering, is vital. Even with layered defenses, some phishing emails will arrive in inboxes, so employees need to be taught the skills they need to help them identify email threats. Employees should then be tested by conducting phishing email simulations. That allows businesses to find out if the training has been taken on board. Without training and testing, employees will remain a liability. Over time their phishing identification shills will improve.
It is worth noting that security awareness training for employees is a requirement of HIPAA, yet many employees are still fooled. Training and phishing simulations can help reduce an organization’s susceptibility to phishing attacks, but employees, being human, will still make mistakes.
The solution is layered defenses. No one cybersecurity solution will block all phishing attempts, and certainly not without also blocking many legitimate email communications. Multiple solutions are therefore required.
It is essential for advanced email security defenses to be implemented to block phishing emails and make sure phishing and malspam (spam emails containing malware) never reach inboxes. That means an advanced spam filtering solution is a must.
SpamTitan for has been independently tested and shown to block in excess of 99.9% of spam emails and 100% of emails containing known malware. SpamTitan also blocks zero-day threats using a combination of advanced detection techniques. This is achieved through heuristic analyses, blacklists, trust scores, greylisting, sandboxing, DMARC, and SPF to name just a few.
SpamTitan has also been developed to compliment Office 365 security and provide a greater level of protection against phishing and other malicious email threats. It should be noted that Microsoft’s Exchange Online Protection was recently shown to allow 25% of phishing emails through.
Should phishing emails arrive in inboxes and be opened by end users, other controls are required to prevent clicks from resulting in malware infections or the theft of credentials. Here a web filtering solution such as WebTitan is important. When a link in an email is clicked, before the webpage is displayed, the URL and the content of the webpage is checked and the user is prevented from visiting the webpage if it, or its domain, is associated with phishing or malware distribution. Malware downloads can also be blocked from websites, even those with a high trust score. Together these solutions form the backbone of your phishing defenses. Further, these two solutions are quick and easy to implement, simple to use and maintain, and they are inexpensive.
Add antivirus protection, multi-factor authentication, and end user training, and you will be well protected from phishing and email and web-based malware attacks.
For further information on improving your defenses against phishing, spear phishing, and malware, give the TitanHQ team a call today.
If you are a managed service provider, contact the TitanHQ channel team and discover why TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email and web security solutions for MSPs serving the SMB market.
by titanadmin | Dec 16, 2019 | Industry News, Spam News, Spam Software
Over the past 2 decades TitanHQ has been developing powerful cybersecurity solutions for SMBs and managed service providers (MSPs) that serve the SMB market. Naturally at TitanHQ we have great belief in our email security solution, SpamTitan. We believe it is the ideal spam filtering solution for SMBs and MSPs for preventing a myriad of email threats from reaching inboxes.
TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email security to MSPs serving the SMB market. We regularly receive positive feedback from MSPs and SMBs about how the solution has saved them hours of work compared to other email security solutions and has helped them improve email security and block more spam and stop malware and ransomware from reaching inboxes.
Positive feedback from end users proves we are getting it right and it inspires us to continue improving the solution to ensure it will keep on protecting our customers from malware, ransomware, viruses, botnets, and social engineering and phishing attacks for many years to come.
The positive feedback is not only provided to our engineers and customer service and sales teams. IT decision makers have posted highly positive reviews on the top business software review platforms and are letting other IT professionals know about their experiences implementing the solution, integrating it with their other cybersecurity solutions and management platforms, and what it is like to use SpamTitan on a daily basis.
In fact, across the different business review sites, SpamTitan has consistently received high scores. There is no other email security product on the market that has achieved such a wealth of positive reviews and feedback from end users.
Some of the positive reviews across the leading business software review sites are detailed below:
Gartner Peer Insights
Gartner Peer insights is one of the most highly respected review platforms from the world’s leading business advisory and research company. While Gartner strictly polices the review site, Gartner is unbiassed and has no hidden agenda. The review platform gives IT professionals the opportunity to give their honest feedback on software solutions that they have implemented to help other IT professionals save time and money in their search.
36 qualified users of SpamTitan have left reviews on the site and the solution has achieved highly positive feedback with an average user score of 4.7 out of 5.
“SpamTitan has been a very responsive vendor to work with, both during the sales process and with post-sales support. Tickets are responded to within several hours and often resolved within a day. The product itself is very MSP-friendly supporting delegation to client admins, multiple delivery pools, and attractive pricing. The catch rate is better than Exchange Online.”
Microsoft Team Lead in the Services Industry
“SpamTitan takes a little technical knowhow, but it’s powerful, flexible and affordable.” Director of IT and Telecom in the Healthcare Industry.
“SpamTitan is superb giving control back to the user and giving time back to IT staff. The product is amazing, it stopped 99% of spam and gives total control back to the user, it is web based and was easy to migrate to. The support and migration management from TitanHQ was brilliant.” IT Security Manager in the Manufacturing Industry.
G2 Crowd
G2 Crowd is one of the leading business software review sites. 139 verified users of SpamTitan have left reviews on the site and the solution has achieved an overall score of 4.6 out of 5. SpamTitan has been rated consistently highly in all rating categories, achieving 9.3 out of 10 for meets requirements and ease of doing business with, 9.2 for ease of setup and quality of support, 9.1 for ease of use, and 9.0 for ease of admin.
Additionally, each quarter, G2 Crowd compiles its Email Security Grid and rates solutions based on customer feedback and market presence. For four consecutive quarters, SpamTitan has been the Top Email Security Solution.
“I really like the customization that is available for this product. We have total control over the spam filter environment for all our customers. The environment is stable which is very important to us and our customers. The support staff was great when we were getting our environment configured. They were quick to reply to emails and reach out to assist us as needed. The spam filtering is top-notch and much better than other products we have used.”
Jeff Banks, Director Of Technology.
Antispam that is affordable, flexible and powerful.” Mike S, Director of IT and Telecommunications.
“Cloud Version is Great for Managed Service Providers.” Andrew B, Vice President.
“Minimizes our exposure to harmful malware and junk emails.” David C, Outreach Specialist.
Google Reviews
112 users of SpamTitan have taken the time to submit their feedback to Google Reviews. The solution is consistently given top marks by users and has achieved an overall review score of 4.9 out of 5.
Some of the positive feedback from users includes:
“TitanHQ is an excellent solution which ticks many boxes. It’s simple to setup, and gives a huge range of functionality all from within one place. My experience of the Support help desk has been great with a team that really do know their product. I highly recommend TitanHQ.” Chris Bell.
“The Titan Span filter is by far one of the best email filters I have ever used. It was simple to setup, it allows users to release their own emails from quarantine quick and easy.” Joseph Walsh.
“Great product. Spam reduced to almost zero and no user complaints. Configuration is simple and support is awesome. Love it!” George Homme.
Capterra
Capterra is a leading software review site that has been active for 20 years. The site has now been purchased by Gartner which moderates reviews on the site. Capterra includes more than 700 categories of software products and is one of the most highly respected business software review sites. It is relied upon by IT decision makers the world over.
SpamTitan has been reviewed by 379 users and has achieved an overall review score of 4.6 out of 5.
“It’s as close to “set it and forget it” as you can come in the IT field. Right out of the box support helped me set everything up in less than 20 minutes, no hardware to worry about, nothing like that. Literally all I have to do is check to see if something was blocked incorrectly once in a while, white list it, and done. I’ve been using spam titan for almost a year and in that time we have blocked over 200k spam/malicious emails for a 30 person company before they even hit employee mailboxes. I shut off the service for 48 hours just to make sure it easy legit, it was, and I haven’t shut it off again since. Whitelisting and blacklisting domains and specific emails are super easy. Support Staff are awesome and go into detail when resolving problems if they were to arise or even if you just have a question. They have always been friendly and courteous and super personable and have been some of the best people to work with in all my years doing IT.” Benjamin Jones, Director Of Information Technology.
“SpamTitan has saved me, saved my company time, and has some of the best support people around. It’s as close to “set it and forget it” as you can come in the IT field. Right out of the box support helped me set everything up in less than 20 minutes, no hardware to worry about, nothing like that. Literally all I have to do is check to see if something was blocked incorrectly once in a while, white list it, and done. I’ve been using spam titan for almost a year and in that time we have blocked over 200k spam/malicious emails for a 30 person company before they even hit employee mailboxes.” Benjamin J, Director of Information Technology.
Spiceworks
Members of the Spiceworks community have also rated SpamTitan highly. The solution has been reviewed by 56 users and has an overall rating of 4.6 out of 5.
Software Advice
The software review site Software Advice includes 350 reviews of SpamTitan from business users and has achieved an average score of 5.58 out of 5.
SpamFilterReviews
According to SpamFilterReviews, SpamTitan is the top-rated spam filtering solution on the site with a score of 4.9 out of 5.
by titanadmin | Dec 13, 2019 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Spam News
Cyberattacks on managed service providers have been increasing over the past few months and they are now a key target for hackers. If a hacker can gain access to the systems of a managed service provider, their remote administration tools can be used to launch attacks on their clients.
There have been several major cyberattacks on managed services providers in the past few weeks, with nation-state-backed hacking groups targeting MSPs serving enterprises and ransomware gangs are conducting attacks on MSPs serving small and medium-sized businesses.
Three major cyberattacks on managed service providers serving healthcare organizations in the United States have been reported in the past two months. All three have affected more than 100 healthcare clients and one impacted 400.
In late November, the Milwaukee-based managed IT service provider, Virtual Care Provider Inc., was attacked with Ryuk ransomware. The attack started on November 17, 2019, and affected all of its clients’ data. Around 110 nursing homes and acute care facilities were prevented from accessing their patients’ medical records. The consequences for its clients were dire. Assisted living facilities and nursing homes were prevented from billing for Medicaid, which meant essential funding was not provided and nursing homes were prevented from ordering essential drugs for patients. Virtual Care Provider was issued with a $14 million ransom demand, which the company could not afford to pay. The managed service provider had around 20% of its services affected and had to rebuild around 100 servers.
The ransomware was deployed as a secondary payload by the TrickBot Trojan. TrickBot had been installed on its network 14 months previously via a malicious email attachment.
A few weeks later, a Colorado-based managed service provider serving dental practices was attacked with ransomware. Complete Technology Solutions was infected with a ransomware variant called Sodinokibi. First, the MSP was attacked, and then its remote administration tools were used to deploy ransomware on the networks of more than 100 dental practices. A ransom demand of $700,000 was issued, which the MSP refused to pay. Its clients are now having to pay the attackers for the keys to decrypt their files. Only a few that had backups stored off the network were able to recover without paying the ransom.
This is the second such attack to affect a company serving the dental industry. The dental record backup service provider, PerCSoft, was also attacked with Sodinokibi ransomware. That attack affected approximately 400 dental practices. CyrusOne was also attacked with Sodinokibi ransomware and its managed services division and six of its clients were affected.
It is not only ransomware that is being used in the attacks. Nation-state threat groups such as APT10 are also targeting MSPs. Their aims are different. The attacks are being conducted to gain access to the intellectual property of their enterprise customers.
As cyberattacks on managed service providers increase, MSPs must ensure that they have adequate defenses in place to keep the hackers at bay. This is an area where TitanHQ can help. TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email and web security solutions for managed service providers that serve the SMB market.
TitanHQ offers a trio of solutions for MSPs under the TitanShield program. SpamTitan email security is a powerful cloud-based solution that keeps inboxes free of spam, phishing emails, and malware. SpamTitan incorporates SPF and DMARC to block email impersonation attacks, dual antivirus engines to detect known malware threats, and heuristics and sandboxing to identify and block zero-day threats.
WebTitan Cloud is a 100% cloud-based DNS filtering solution that works seamlessly with SpamTitan to block web-based phishing attacks and malware downloads. The solution allows you to monitor and identify malicious threats in real-time and includes AI-driven protection against active and emerging phishing URLs, including zero-minute threats.
The third solution is ArcTitan, a cloud-based email archiving solution that provides protection against data loss and helps MSPs and their clients meet their compliance obligations. ArcTitan serves as a black box flight recorder for email and stores email data securely in the cloud on Replicated Persistent Storage on AWS S3. When emails need to be searched and recovered, the searches are lightning-fast. ArcTitan can search up to 30 million emails a second.
ArcTitan has recently been moved to a brand new system, with the service delivered as a highly available, self-healing horizontally scaled Kubernetes cluster. Within that cluster are many different components working in harmony together, but independently. Should any component go down, that component can be taken offline and repaired with no impact on the others, ensuring a much more reliable service with minimal or no disruption during an outage. With ArcTitan, email is protected from cyberattacks.
These solutions are not only an ideal for improving the security posture of MSP clients, they can help to ensure that MSP systems are protected from attack. All TitanHQ solutions are quick and easy to implement, have a low management overhead, and are API-driven so they can easily be incorporated into MSP’s remote management and monitoring systems.
To find out more about the TitanShield program for managed service providers and to discover how TitanHQ’s cybersecurity solutions can improve yours and your clients’ security posture, give the TitanHQ channel team a call today.
by titanadmin | Nov 30, 2019 | Email Scams, Internet Security, Spam Advice, Spam News
Recent research has highlighted just how important it is for businesses to implement a range of defenses to ensure phishing emails are not delivered to inboxes and how business phishing protections are failing.
The studies were conducted to determine how likely employees are to click on phishing emails that arrive in their inboxes. Alarmingly, one study indicated almost three quarters of employees were fooled by a phishing test and provided their credentials to the attacker. In this case, the attacker was the consultancy firm Coalfire.
71% of the 525 businesses that were tested had at least one employee disclose login credentials in the phishing test, compared to 63% last year. At 20% of businesses, more than half of the employees who were tested fell for the phishing scam, compared to 10% last year.
A second study conducted by GetApp revealed a quarter of 714 surveyed businesses said they had at least one employee who responded to a phishing attack and disclosed their login credentials and 43% of businesses had employees that had clicked on phishing emails. The study also revealed only 27% of businesses provide security awareness training to employees, only 30% conduct phishing simulations, and 36% do not have multi-factor authentication in place on email.
The Importance of Layered Phishing Defenses
To mount an effective defense against phishing and other cyberattacks, a defense in depth approach to security is required.
With layered defenses, businesses are not replying on a single solution to block phishing attacks. Multiple defenses are put in place with the layers overlapping. If one measure proves to be ineffective at blocking a phishing email, others are in place to provide protection.
One area where many businesses fail is relying on Office 365 anti-phishing controls. A study by Avanan showed Office 365 phishing defenses to be effective at blocking most spam emails, but 25% of phishing emails were delivered to inboxes.
What is required is an advanced anti-spam and anti-phishing platform that can be layered on top of Office 365 to ensure that these phishing emails are blocked. SpamTitan can be seamlessly implemented in Office 365 environments and provides superior protection against phishing and malware attacks. SpamTitan blocks more than 99.9% of spam and phishing emails, 100% of known malware, and incorporates a host of features to identify zero-day threats.
As good as SpamTitan is at blocking email threats, other layers should be implemented to block phishing attacks. If a phishing email arrives in an inbox, a web filter will provide protection by blocking attempts by employees to visit phishing websites and sites hosting malware. WebTitan is a powerful DNS filtering solution that protects against the web-based element of phishing attacks. WebTitan adds an extra layer to phishing defenses and will block attempts by employees to visit malicious sites.
If an attacker succeeds in obtaining the credentials of an employee, it is important that those credentials cannot be used to gain access to the account. That protection is provided by multi-factor authentication. Multi-factor authentication is not infallible, but it will prevent stolen credentials from being used to access accounts in the majority of cases.
Security awareness training is also vital. Employees are the last line of defense and that defensive line will be tested. If employees are not trained how to identify phishing emails and other email security threats, they cannot be expected to recognize threats when they land in inboxes. An annual training session is no longer enough, considering how many phishing attacks are conducted on businesses and how sophisticated the attacks are becoming.
Security awareness training should consist of an annual training session with regular refresher training sessions throughout the year. Employees should be kept up to date on the latest tactics being used by cybercriminals to help them identify new scam emails that may bypass email security defenses. Phishing simulation exercises are also important. If these simulations are not conducted, businesses will have no idea how effective their training sessions have been, and which employees have not taken the training on board.
by titanadmin | Nov 27, 2019 | Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
A new phishing campaign has been detected that is targeting Office 365 admins, whose accounts are far more valuable to cybercriminals than standard Office 365 accounts.
A standard Office 365 email account can used for spamming or conducting further phishing attacks on the organization or business contacts. However, there is a problem. When the account is used for phishing, the sent messages are likely to be noticed by the user. Failed delivery messages will also arrive in the user’s inbox. The account may only be able to be used for a short time before an account compromise is detected.
The attackers targeting Office 365 admins aim to compromise the entire domain. Office 365 admins can create new accounts on the domain, which are then used for phishing. Since the only person using that account is the attacker, it is likely the malicious actions will not be noticed, at least not as quickly. The only person who will see the failed delivery messages and sent emails is the attacker.
The newly created account abuses trust in the business domain. Any individual to receive such a phishing message may mistakenly believe the email is a legitimate message from the company. The messages also take advantage of the reputation of a business. Since the business domain will have been used only to send legitimate messages, the domain will have a high trust score. That makes it far more likely that the emails being sent from the new account will be delivered to inboxes and will not be picked up by Office 365 spam filters. The Office 365 admin may also have access to all email accounts on the domain, which will allow the attacker to steal a huge amount of email data.
In theory, Office 365 admins should be better at identifying phishing emails than other employees in the organization as they usually work in the IT department; however, these emails are very realistic and will likely fool many Office 365 admins.
The lure being used is credible. The emails appear to have been sent by Microsoft and include the Microsoft and Office 365 logos. The emails claim that the organization’s Office 365 Business Essentials invoice is ready. The user is told to sign into the Office 365 admin center to update their payment information, set their Message Center preferences, and edit their release preferences or join First Release and set these up if they have not done so already. The emails include an unsubscribe option and are signed by Microsoft and include the correct contact information. The emails also link to Microsoft’s privacy statement.
The embedded hyperlinks in the emails link to an attacker-controlled domain that is a carbon copy of the official Microsoft login page. If the user’s credentials are entered, they are captured by the attacker.
This campaign highlights how important it is to have layered email security defenses in place to block phishing attacks. Many phishing emails bypass standard Office 365 anti-phishing controls so additional protection is required.
An advanced anti-phishing solution such as SpamTitan should be layered on top of Office 365 to provide greater protection against sophisticated phishing attacks. Approximately 25% of all phishing emails bypass standard Office 365 phishing protections.
Another anti-phishing layer that many businesses have yet to implement is a web filter. A web filter, such as WebTitan, provides protection when messages are delivered to inboxes, as it blocks attempts by employees to visit phishing websites. When a link to a known phishing website is clicked, or the user attempts to visit a questionable domain, they will be directed to a block page and the phishing attack will be blocked.
by titanadmin | Nov 26, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Advice, Spam News, Spam Software
The aim of this post is to provide you with some easy to adopt email security best practices that will greatly improve your organization’s security posture.
Email is the Most Common Attack Vector!
It is a certainty that business email systems will be attacked so email security measures must be implemented. The best form of email security is to do away with email altogether, but since businesses rely on email to communicate with customers, partners, and suppliers, that simply isn’t an option.
Email not only makes it easy to communicate with the people you need to for your business to operate, it also allows cybercriminals to easily communicate with your employees and conduct phishing attacks, spread malware and, if a corporate email account is compromised, communicate with your customers, partners and suppliers.
Email security is therefore essential, but there is no single solution that will protect the email channel. A spam filtering solution will stop the majority of spam and malicious email from reaching inboxes, but it will not block 100% of unwanted emails, no matter what solution you implement. The key to robust email security is layered defenses. If one defensive measure fails, others are in place that will provide protection.
You need a combination of technical, physical, and administrative safeguards to secure your email. Unfortunately, there is no one-size-fits-all approach that can be adopted to secure the email channel but there are email security best practices that you can adopt that will improve your security posture and make it much harder for cybercriminals to succeed.
With this in mind, we have outlined some of the most important email security best practices for your business and your employees to adopt.
Email Security Best Practices to Implement Immediately
Cybercriminals will attempt to send malware and ransomware via email, and phishing tactics will be used to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, so it is important to be prepared. Listed below are 8 email security best practices that will help you keep your email system secure. If you have not yet implemented any of these best practices, or have only done so partially, now is the time to make some changes.
Develop a Cybersecurity Plan for Your Business
We have included this as the first best practice because it is so important. It is essential for you to develop a comprehensive cybersecurity plan for your entire organization as not all threats arrive via email. Attacks come from all angles and improving email security is only one of the steps you need to take to improve your overall cybersecurity posture.
There are many resources available to help you develop a cybersecurity plan that addresses all cyber risks. The Federal Communications Commission has developed a Cyberplanner to help with the creation of a custom cybersecurity plan and the Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has recently issued a Cyber Essentials Guide for Small Businesses and Governments. Take advantage of these and other resources to develop an effective cybersecurity plan.
Implement an Advanced Spam Filtering Solution
A spam filter serves as a semi-permeable membrane that prevents email threats from being delivered to inboxes and lets genuine emails pass through unimpeded. This is the single most important security measure to implement to protect against email threats and productivity-draining spam.
If you use Office 365 you will already have some protection, as Office 365 includes a spam filter and anti-virus software, but it falls short on phishing protection and will not block zero-day malware threats. You need layered defenses to secure email which means a third-party spam filter should be used on top of Office 365. Research from Avanan showed that 25% of phishing emails bypass Office 365 defenses.
There are many spam filtering services for SMBs, but for all-round protection against known and zero-day threats, ease of implementation, ease of use, and price, SpamTitan is the best choice for SMBs.
Ensure Your Anti-Virus Solution Scans Incoming Emails
You will no doubt have anti-virus software in place, but does it scan incoming emails? Email is one of the main ways that malware is delivered, so anti-virus software for email is a must. This does not necessarily mean you need a different antivirus solution. Your existing solution may have that functionality. Your spam filter is also likely to include AV protection. For example, SpamTitan incorporates dual anti-virus engines for greater protection and a sandbox where email attachments are analyzed for malicious actions. The email sandbox is used to detect and block zero-day malware – New, never-before-seen malware variants that have yet to have their signatures incorporated into AV engines.
Create and Enforce Password Policies
Another obvious email security best practice is to create a password policy that requires strong passwords to be set. There is no point in creating a password policy if it is not enforced. Make sure you implement a control measure to prevent weak passwords from being set. Weak passwords (password, 123456, or dictionary words for example) are easy to remember but also easy to guess. Consider that cybercriminals are not sitting at a computer guessing passwords one at a time. Automation tools are used that make thousands of password guesses a minute. It doesn’t take long to guess a weak password! You should also make sure rate limiting is applied to block an IP from logging in after a set number of failed login attempts.
It is a good best practice to require a password of at least 8 characters to be set, with a combination of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols, and to block the use of dictionary words. Consider allowing long passphrases to be used as these are easier for employees to remember. Check the National Institute of Science and Technology (NIST) advice on secure password practices if you are unsure about creating a password policy.
Implement DMARC to Stop Email Impersonation Attacks and Domain Abuse
DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance to give it its full name, is an email protocol that uses Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to determine whether an email is authentic.
By creating a DMARC record you are preventing unauthorized individuals from sending messages from your domain. DMARC also lets you know who is sending messages from your domain, and it lets you set a policy to determine what happens to messages that are not authenticated, I.e. quarantine them or reject them. Some email security solutions, such as SpamTitan, incorporate DMARC authentication.
Not only DMARC help you block email impersonation attacks, it also prevents abuse of your domain. Your DMARC record tells receiving email servers not to accept messages sent from authenticated users, thus helping protect your brand.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication is yet another layer you can add to your anti-phishing defenses. Multi-factor authentication, as the name suggests, means more than one method is used to authenticate a user. The first factor is usually a password. A second factor is also required, which is something a person knows or possesses. This could be a mobile phone, to which a one-time PIN code is sent, or a token on a trusted device.
This safeguard is vital. If a password is obtained, in a phishing attack for example, the password alone will not grant access to the email account without an additional factor being provided. A combination of a password, token, and one-time PIN is a good combination.
Train Your Employees and Train Them Again
No matter how tech savvy your employees appear to be, assume they known nothing about cybersecurity. They will certainly not routinely stick to email security best practices unless you train them to do so and then hammer the message home.
Before letting any employee have access to email, you should provide security awareness training. Your training should cover email security best practices such as never opening email attachments from unknown senders, never enabling content in documents unless the document has been verified as legitimate, and never to click hyperlinks in emails or send highly sensitive information such as passwords via email.
You must also train your employees how to recognize phishing emails and other malicious messages and tell them what to do when suspicious emails are received. Anyone with access to email or a computer must be provided with security awareness training, from the CEO down.
One training session is not enough. Even an annual training session is no longer sufficient. You should be providing regular training, be sending cybersecurity newsletters warning about the latest threats, and using other tools to help create a security culture in your organization.
Conduct Phishing Awareness Simulation Exercises
You have provided training, but how do you know if it has been effective? The only way to tell is to conduct tests and that is easiest with phishing simulation exercises. These are dummy phishing emails that are sent to employees when they are not expecting them to see how they respond. You maybe surprised at how many employees respond and disclose sensitive information, open attachments, or click links in the emails.
The aim of these emails is to identify people that have not taken their training on board. The idea is not to punish those employees, but to tell you who needs further training. There are several companies that can assist you with these exercises. Some even offer free phishing simulation emails for SMBs.
TitanHQ is Here to Help!
TitanHQ has developed SpamTitan to be easy for SMBs to implement, use, and maintain. It requires no hardware, no software, and all filtering takes place in the cloud. Not only does SpamTitan offer excellent protection against the full range of email-based threats, it is also one of the lowest cost solutions for SMBs to implement.
Give the TitanHQ team a call today for more information on SpamTitan and to find out about how you can also protect your business from web-based threats and meet your compliance requirements for email.
by titanadmin | Nov 26, 2019 | Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Advice, Spam Software
SMBs and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) that serve the SMB market have many spam filtering services to choose from. In this post perform a VadeSecure vs SpamTitan Email Security comparison to help you decide on the best solution to meet the needs of your business.
Who are VadeSecure?
VadeSecure is a French company that was founded in 2009. The company has developed a predictive email defense solution to protect businesses from email-based threats and spam email, and also consumers through their ISPs. The company has yet to make great inroads in the MSP market, although that is part of the company’s plan, having recently raised $79 million in venture capital to help them achieve this aim.
SpamTitan Email Security from TitanHQ
TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email and web security solutions for MSPs that serve the SMB market. TitanHQ has more than 2 decades of experience in email and web security and has developed two award winning solutions for MSPs – WebTitan (Web Security) and SpamTitan Email Security. Here we will focus on SpamTitan Email Security.
VadeSecure vs SpamTitan Email Security
Take a quick look at VadeSecure and SpamTitan Email Security and you may think that both solutions are very similar, and in some respects they are. Both are cloud-based email security solutions that have been designed to block email threats and keep inboxes free from spam and malicious messages and attachments. Both solutions have been developed to provide an additional security layer for Office365 to block the many spam and malicious messages that bypass O365 security controls.
However, there are some very important differences between the solutions as far as MSPs are concerned. VadeSecure has been developed solely for the Telco market, but MSPs have unique requirements that are not well catered to. A deeper dive into the products and a more thorough comparison of VadeSecure vs SpamTitan Email Security from an MSP perspective reveals the two solutions are very different products.
SpamTitan is very much MSP focused. Over time, with the increased investment, VadeSecure may become a more MSP friendly solution, but as it stands VadeSecure and SpamTitan Email Security are not equivalent solutions.
Comparison of VadeSecure and SpamTitan Email Security for MSPs
SpamTitan Email Security has been developed by MSPs for MSPs. SpamTitan Email Security is therefore a very MSP-focused product, which incorporates many MSP-friendly features. SpamTitan is a true multi-tenant solution. With SpamTitan Email Security, MSPs are given a multi-tenancy view of all customers with multiple management roles. This allows MSPs to easily monitor all customer deployments and the trial-base, assess the health of those deployments, view activity volumes across your entire customer base, and quickly identify any issues that need to be addressed. VadeSecure lacks this customer-wide view of the system and does not integrate with RMMs or PSAs.
Configurability and Customization Potential
Configurability is also a key consideration. VadeSecure is not easily configurable to meet your needs. For instance, it does not support custom rules, so you have to use Office 365 Exchange admin functionality for configuration. In a similar vein, the potential for customization is limited with VadeSecure. With SpamTitan Email Security, there is plenty of scope for customization. You can create custom rules to meet the needs of your customer base thanks to highly granular controls that can be applied to domains, groups, or individual users. This level of granularity is important, as it allows you to carefully configure the solution to meet the needs of each client. You can tailor the solution to suit the risk tolerance of each individual client and adopt a more aggressive or more permissive approach on a per client basis and minimize false positives and false negatives. VadeSecure lacks the granularity to allow this for each customer.
Management and Reporting
You are implementing email security to provide your customers with greater security, but you need to make sure the solution remains effective over time. You will therefore need to identify issues as they arise and perform tweaks to continue to protect your clients to the highest degree. To achieve this, you need highly granular reports. Without them you will not have the visibility you need. SpamTitan’s suite of pre-configured and customizable reports give you full visibility into your deployments to allow you to quickly identify and correct any issues.
You can also generate reports (manually or automatically) that you can send to your clients to show them how effective the solution is, the threats that are being blocked, and why continued protection is essential. With VadeSecure you lack this visibility and cannot find out what has been blocked for end users or obtain detailed information on spam emails and threats. Client management is also more difficult with VadeSecure. MSPs need to login to each client’s Office 365 environment for management, which makes reporting much more time consuming.
Revenue Potential and Margins
Because SpamTitan allows MSPs to customize their deployments, MSPs have superior management capabilities and can offer clients greater value, which means greater margin potential for MSPs. It also makes it harder for clients to switch providers as their MSP is more of a strategic partner rather than just an IT service provider.
With TitanHQ there is also greater potential to make more margin by cross selling other services. MSPs that sign up with TitanHQ and join the TitanShield program have access to two other revenue generating solutions: WebTitan DNS filtering and ArcTitan Email Archiving. These allow you to maximize monthly recurring revenue with each client. Additional revenue-generating solutions are not available with VadeSecure.
VadeSecure Vs SpamTitan Email Security Pricing
Currently, pricing with VadeSecure is complex and the solution is expensive for MSPs. VadeSecure is charged on a per module basis, which means you need to factor in a lot of additional costs, such as anti-virus protection and GreyMail which are not included as standard. With SpamTitan there is one flat fee that includes all features of the solution. TitanHQ pricing is totally transparent and there are no hidden extras.
After speaking with customers that have tried VadeSecure, we have learned that the total number of users are not aggregated into the MSP discount with VadeSecure. You could have 100 x 10-seat licenses (1,000 users), but VadeSecure pays at 10 seats each and not the 1,000 seats overall. In contrast, TitanHQ’s appreciates how MSPs work and has developed a flexible pricing policy accordingly.
Quick Comparison of Features
In the image below we have compared the basic features of both SpamTitan and VadeSecure as a quick reference to show you some of the key differences between VadeSecure and SpamTitan Email Security.
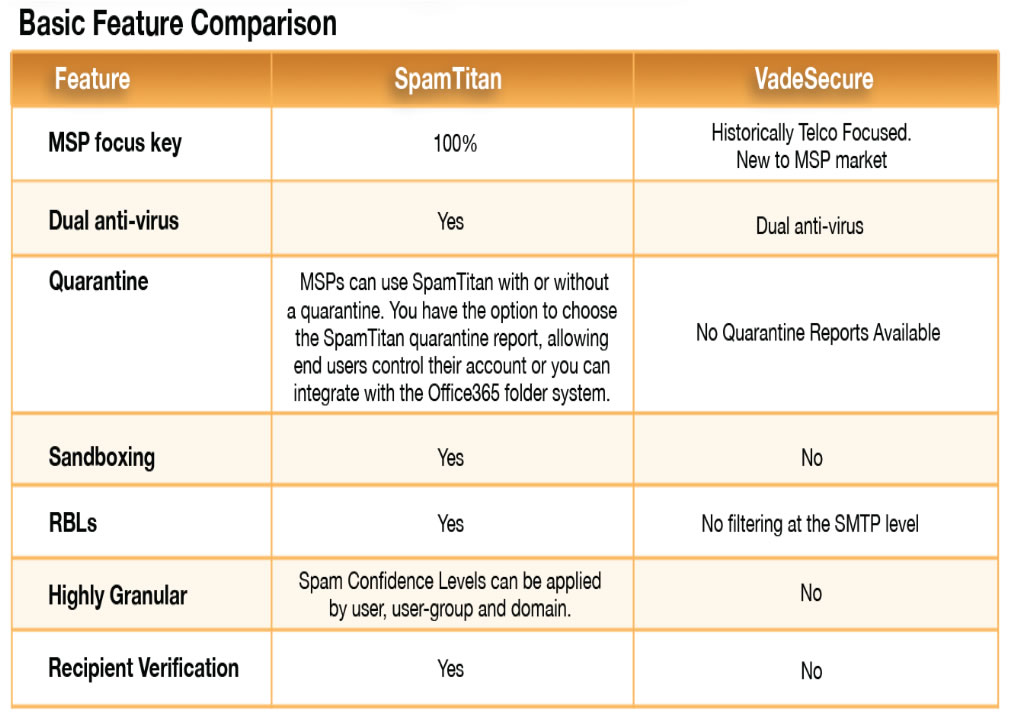
MSPs that serve customers with Office 365 environments should adopt a layered approach to security and should not rely on the anti-spam and anti-phishing defenses incorporated into Office 365. Additional layers are required to better protect clients, which will mean you spend less time on support and remediating phishing attacks.
TitanHQ can provide two additional layers to your security stack: SpamTitan and WebTitan, both of which work seamlessly together to protect against all email and web-based threats.
To find out more about these solutions, how you can reduce the cost of email security and web security for your customers while earning a profitable margin, contact the TitanHQ team today and ask to speak to the channel team.
by titanadmin | Nov 18, 2019 | Internet Security, Network Security, Spam Advice, Spam Software, Website Filtering
Cybercriminals are inventive and their attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated. To help ensure you are prepared and can defend your business against these attacks, we have listed the top 10 cybersecurity threats your business is likely to face, along with some tips to help you prevent a costly data breach.
Cybercriminals are not just trying to attack large enterprises. Sure, a cyberattack on a large healthcare system or blue-chip company can be incredibly rewarding, but the defenses they have in place make attacks very difficult. SMBs on the other hand have far fewer resources to devote to cybersecurity and as a result they are easier to attack. The potential rewards may not be as great, but attacks are more likely to succeed which means a better return on effort. That is why so many SMBs are now being attacked.
There is a myriad of ways that a company can be attacked, and the tactics, techniques and procedures used by cybercriminals are constantly changing. The top 10 cybersecurity threats listed below include the main attack vectors that need to be blocked and will serve as a good starting point on which you can build a robust cybersecurity program.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats Faced by SMBs
We have listed the top 10 cybersecurity threats that SMBs need to defend against. All the threats listed below need to be addressed as any one of them could easily result in a costly data breach, data loss, or could cripple your business. Some of the threats listed below will be harder to address than others, and it will take time for your cybersecurity defenses to mature. The important thing is to start the ball rolling and address as many of these areas as soon as possible.
Human Error and Insider Threats
We have listed human error first, as it doesn’t matter what hardware and software solutions you implement, human error can easily undo much of your good work. Mistakes will be made by employees on occasion. What you need to do is reduce the potential for errors and limit the harm that can be caused.
Developing robust policies and procedures and providing training will help to ensure that your employees know how to act and more importantly, how not to.
Mistakes are not the only thing you need to take steps to try to prevent. There may also be individuals on your payroll who will take advantage of poor security for personal gain. You will also need to tackle the problem of insider threats and make it harder for rogue employees to cause harm and steal data. The measures listed below will help address threats from within and reduce risk.
- Passwords
- Enforce the use of strong passwords but make it easier for your employees to remember them so they don’t try to circumvent your password policy or, heaven forbid, write their passwords down. Implement a password manager to store their passwords so they only have one password or pass phrase to remember.
- Rule of Least Privilege
- It is obvious, but often overlooked. Don’t give employees access to resources they do not need for their day-to-day work duties. If their credentials are compromised, this will limit the harm caused. It will also limit the harm that can be caused by rogue employees.
- Block the Use of USB Devices
- USB devices make it easy for rogue employees to steal data and for malware to be accidentally or deliberately be introduced. Implement technical controls to prevent USB devices from being connected, and if they are required for work purposes only give permission to certain individuals to use them. Ideally, use more secure methods of transferring or storing data.
- Monitor Employee Activity
- If rogue employees are stealing data, you are only likely to find out if you are monitoring their computer activity. Similarly, if credentials are compromised, system logs will highlight any suspicious activity. Make sure logs are created and monitored. Consider using a security information and event management (SIEM) solution to automate this as much as possible.
- Terminate Access at Point of Termination
- Terminating an employee? Terminate their access to your systems at the point of termination. It is surprising how often employee access rights are not terminated for days, weeks, or even months after an employee has left the company.
We will cover some more important safeguards to implement to protect against user error in the following 9 SMB cybersecurity threats.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing is arguably the biggest cybersecurity threat faced by SMBs. Phishing is the use of social engineering techniques to persuade people to divulge sensitive information or take an action such as installing malware or ransomware. This is most commonly achieved via email, but can also occur via text messages, social media websites, or over the telephone.
Do not assume that your employees have common sense and know not to open email attachments from unknown individuals or respond to enticing offers from legal representatives of Nigerian princes. You must train your employees and teach cybersecurity best practices and show them how to identify phishing emails. Refresher training should be provided at regular intervals and you should conduct phishing simulation exercises (which can largely be automated) to find out who has taken the training on board and who is a liability that needs further training.
Employees are the last line of defense. You need a layer of security above your employees to make sure their security awareness training is never required. That means an advanced anti-spam solution needs to be in place to block threats before they reach inboxes. If you use Office 365, you should still implement an antispam solution. A recent study by Avanan revealed 25% of phishing emails bypass Office 365 antispam defenses.
Another layer of protection should also be implemented to protect against phishing: Multi-factor authentication. This is the use of an additional authentication factor that will kick into action if an attempt is made to use credentials from an untrusted device or location. If credentials are compromised in a phishing attack, multi-factor authentication should stop them from being used to gain access to email accounts, computers, or network resources.
Malware and Ransomware
Malware, viruses, ransomware, spyware, Trojans, worms, botnets, and cryptocurrency miners are all serious threats that you must take steps to block. It goes without saying, but we will say it none the less, you need to have antivirus software installed on all endpoints and your servers.
Malware can be installed in many ways. As previously mentioned, blocking USB devices is important and spam filtering software with sandboxing will protect you from email-based attacks. Most malware infections now occur via the internet, so a web filtering solution is also important. This will also add an extra layer to your phishing defenses. A web filter will block drive-by malware downloads, prevent employees from visiting malicious sites (including phishing websites) and also allows you to enforce your internet usage policies. A DNS filtering solution is the best choice. All filtering takes place in the cloud before any content is downloaded and it will not add to your patching burden.
Shadow IT
Shadow IT – The term given for any hardware or software in use that has not been authorized by your IT department. This could be a portable storage device such as a zip drive, a VPN client to bypass your web filter, an application to help with work tasks, or all manner of other software. It is surprising to find exactly how many of these programs are installed on users’ devices when IT support staff are called upon to sort out a problem!
So, what is the problem? Anything installed without authorization is a potential security and compliance risk. Your security team has no control over patching, and vulnerabilities in those applications could easily go addressed for months and give hackers an easy entry point into your network. Fake applications could be downloaded that are really malware, software packages often include a host of potentially unwanted programs and spyware, and any data stored in these applications could be transmitted to unsecure locations. Those applications and data contained therein are also unlikely to be backed up by the IT department. If anything happens, data can easily be lost.
Unpatched Software
The importance of prompt patching cannot be understated. Vulnerabilities exist in all software solutions. Sooner or later those vulnerabilities will be found, and exploits will be developed to take advantage. Security researchers are constantly looking for flaws that could potentially be exploited by threat actors to gain access to sensitive information, install malware, or remotely execute code. When these flaws are identified and patches are released, they need to be applied promptly. Oftentimes, vulnerabilities are being actively exploited by the time a patch is released. It is essential for these vulnerabilities to be addressed as soon as possible and for all software to be kept up to date.
When software or operating systems are approaching end of life, you must upgrade. When patches stop being issued and software is unsupported, any vulnerabilities will remain unaddressed and can easily be exploited.
Out of Date Hardware
Not all vulnerabilities come from out of date software. The hardware you use can also introduce risks. You must keep an inventory of all your hardware, so nothing slips through the cracks. Firmware updates should be applied as soon as it is made available and you should monitor for any devices that are approaching end of life. If your devices do not support the latest operating systems, then it is time to replace your hardware. This will naturally come at a cost, but so do cyberattacks and data breaches.
Unsecured IoT Devices
The Internet-of-Things offers convenience but IoT devices are a potential liability. IoT devices can send, store or transmit data so they must be be secured.
Unfortunately, in the hurry to connect everything to the internet device manufacturers often overlook security as do users of these devices. Take security cameras for instance. You may be able to access your cameras remotely, but you may not be the only person who can. If your security cameras are hacked, thieves could see what you have, where it is located, and where and when security is lax. There have been cases of security cameras being hacked due to the failure to change default credentials for remote management.
Ensure you change the default credentials on the devices and use strong passwords. Keep the devices up to date, and if the devices need to connect the network, make sure they are isolated from other resources. Cybercriminals can also take advantage of flaws in the applications to which these IoT devices connect. They must also be kept up to date.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks and Public Wi-Fi
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is an attack scenario where communications between two individuals (or one individual and a website or network) are intercepted and potentially altered. An employee may believe they are communicating securely, when everything they are saying or doing is being seen or recorded. An attacker could even control the conversation between two people and be communicating with each separately while both individuals believe they are communicating with each other. This method of attack most commonly occurs through unsecured Wi-Fi hotspots or evil twin hotspots – Fake Wi-Fi hotspots set up in coffee shops, airports, and any other location where free Wi-Fi is offered.
If you have remote workers, you need to take steps to ensure that all communications are kept private. This can be achieved in two main ways. By making sure employees use a secure VPN that encrypts their communications over public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks and also by implementing a DNS filtering solution. The DNS filtering solution provides the same protection for remote workers as it does for on-premises workers and will prevent malware downloads and employees from accessing malicious websites.
Mobile Security Threats
There is no denying the convenience of mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones). They allow workers to be instantly contacted and lets them work from any location. Mobile devices improve employee mobility, can lead to greater employee satisfaction, and will help you to boost productivity. However, the devices also introduce new risks. Whether you supply these devices or operate a BYOD policy, you need to implement a range of security controls to ensure those risks are managed.
You need to make sure you know of every device that you allow to connect to the network. A mobile device security solution can help you gain visibility into mobile device use and allow you to control your applications and data.
You should ensure the devices have security controls applied, can only access your network via secure channels (VPN), ensure the devices are covered by a DNS filtering solution, and any work data stored on the devices needs to be encrypted.
Remote Desktop Protocol
Remote desktop protocol (RDP) allows employees remotely connect to your computers and servers when they are not in the office and lets your managed service provider quickly sort out your problems and maintain your systems without having to pay a visit. RDP also gives hackers an easy way to gain access your computers, servers, and steal data or install malware. Do you need RDP enabled? If not, disable it. Does it need to be used internally only? Make sure that RDP is not exposed to the internet.
If you do need RDP, then you need to exercise extreme caution. Make sure that users can only connect via a VPN or set firewall rules. Limit the individuals who have permissions to use RDP, ensure strong passwords are set, and that rate limiting is implemented to protect against brute force attacks. Also use multi-factor authentication.
Stolen RDP credentials are often used by hackers to gain access to systems, brute force attempts are often conducted, and vulnerabilities in RDP that have not been patched are frequently exploited. This is one of the main ways that ransomware is installed.
These are just the top 10 cybersecurity threats faced by SMBs. There are many more risks that need to be identified and mitigated to ensure you are protected. However, by addressing the above issues you will have already made it much harder for hackers and cybercriminals to do your business harm.
TitanHQ is Here to Help!
TitanHQ can assist by providing you with advanced cybersecurity solutions to protect against several of the above listed top 10 cybersecurity threats and will the two most commonly used attack vectors – email and the web-based attacks. These solutions – SpamTitan and WebTitan – are 100% cloud based, easy to implement and maintain, and will provide superior protection against malware, ransomware, viruses, botnets, and phishing attacks.
Further, these powerful solutions are affordable for SMBs. You are likely to be surprised to find out how little these enterprise-grade security solutions will cost. If you are a managed service provider that services the SMB market, you should also get in touch. SpamTitan and WebTitan have been developed by MSPs for MSPs. There is a host of reasons why TitanHQ is the leading provider of cloud-based email and web security solutions to MSPs that service the SMB market!
Contact our friendly (and non-pushy) sales team today to find out more, book a product demo, and register for a free trial.
by titanadmin | Nov 18, 2019 | Industry News, Spam Software
TitanHQ has announced that a new version of its award-winning cloud-based anti-spam service and anti-spam software has been released. SpamTitan v7.06 incorporates a new RESTapi to allow clients and partners to seamlessly integrate SpamTitan into their own systems.
The new version was released on November 12, 2019 and has automatically been applied to the cloud-based offering. Users of SpamTitan software will have had the latest version downloaded, although they will need to login to their UI to apply the update.
As part of the regular patching cycle, SpamTitan patches have been released to address reporting engine issues and patches and ISO/OVA images are now available. These have been released for several packages including OpenSSL, OpenSSH, PHP, ClamAV and sudo. The patches must also be applied manually by administrators on their appliance(s).
TitanHQ has had a busy 2019. The company has experienced 30% growth in 2019 and has just had its busiest ever quarter for MSP growth. The growth has been driven by demand from MSPs for easy to use email security and web security solutions to protect their SMB clients from the growing number of cybersecurity threats.
TitanHQ now has more than 2,200 MSP partners using its platform and the strong Q3 growth has continued in Q4 helped by the new “Margin Maker for MSPs” Q4 initiative.
“Implementing the RESTapi and encouraging API adoption are vital steps in our partnership expansion plans,” explained TitanHQ CEO, Ronan Kavanagh. “We have enjoyed a record-breaking growth and the latest enhancements and new features that have been added to SpamTitan will help to ensure growth in 2020 will continue at record levels.”
by titanadmin | Nov 11, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Advice, Spam News
Phishers are constantly changing tactics and coming up with new ways to fool people into handing over their credentials or installing malware. New campaigns are being launched on a daily basis, with tried and tested lures such as fake package delivery notices, fake invoices and purchase orders, and collaboration requests all very common.
In a departure from these common phishing lures, one threat group has opted for a rarely seen lure, but one that has potential to be very effective: Fake court subpoenas. The emails use fear and urgency and are designed to get users to panic and click quickly.
This campaign has been running for a few weeks and is targeting users in the United Kingdom, although this scam could easily be adapted and used in attacks on users in other countries.
Many phishing scams have the goal of stealing credentials to allow email accounts or Office 365 accounts to be accessed. In this case, the aim of the attack is to spread information stealing malware called Predator the Thief.
The phishing emails appear to have been sent by the Ministry of Justice in the UK. The sender field has Ministry of Justice as the display name and the emails have the Ministry of Justice crest, although the actual email address suggests the email has come from the Department of Justice (DOJ).
The emails warn the user that they have been subpoenaed. They are supplied with a case number along with a date when they have been ordered to attend court.
The emails include a hyperlink which the user must click to find out details of the charge and the documents they will need to bring with them to court. Urgency is added by warning the recipient they only have 14 days to respond to provide notice, and that the court case will proceed without them if they do not respond.
The URL in the email is seemingly benign, as it links to Google Docs – a trusted website. Clicking the link will see the user first directed to Google Docs, then redirected to OneDrive. When the user arrives on the OneDrive site, a document is downloaded. That document contains a malicious macro that launches a PowerShell command that downloads Predator the Thief malware.
Predator the Thief is an information stealer that can take screenshots and steals email and FTP credentials, along with cryptocurrency wallets and browser information. In contrast to many browser information stealers, this malware variant doesn’t just target the main browsers, but a host of less popular browsers. Once information has been stolen, the malware cleans up and exits, which makes it harder for the infection to be detected.
Phishing scams such as this highlight the need for layered security. Naturally, an advanced anti-spam solution such as SpamTitan should be implemented to block these threats and ensure and ensure messages are not delivered to end users’ inboxes. SpamTitan also includes DMARC email authentication to block mail impersonation attempts and a sandbox where email attachments are analyzed for malicious actions.
SpamTItan blocks in excess of 99.9% of all malicious emails, but it is not possible to block 100% of threats no matter what email security solution you use. This is where another layer is required. WebTitan is a DNS filtering solution that blocks threats such as this at the point where a DNS lookup is performed. This allows malicious websites to be blocked before any content is downloaded. WebTitan can also be configured to block downloads of certain file types.
With these two solutions in place, your business will be well protected against phishing emails and web-based malware downloads.
by titanadmin | Oct 23, 2019 | Email Archiving, Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Spam Software, Website Filtering
Q3, 2019 has seen TitanHQ register record-breaking growth in the MSP market with its busiest ever quarter for MSP sales. TitanHQ now has more than 2,200 MSP partners and its cloud-based email security, web security, and email archiving platforms are now used by more than 8,200 businesses around the world.
Many great success stories start from humble beginnings, and TitanHQ is no exception. The company started life as Copperfasten Technologies in 1999 and sold anti-spam appliances to local businesses from its Galway, Ireland base. The company then developed its own cybersecurity solutions, starting with the anti-spam and anti-phishing solution, SpamTitan.
The product portfolio grew to include WebTitan web filtering, a powerful DNS-based web security solution to protect businesses from the full range of internet threats. That was followed by the launch of ArcTitan, a cloud-based email archiving solution for businesses that eases their email storage and compliance burden.
That trio of core TitanHQ products has proven to be a massive hit with managed service providers, although not by accident. Many companies have developed innovative solutions for SMBs but have only realized the importance of the MSP market later on. Additional features are then added to appeal to MSPs. TitanHQ took a different approach. Its solutions were developed by MSPs for MSPs and MSPs were considered at every stage of product development. The result is a suite of security solutions tailor-made for MSPs.
This approach, along with cutting-edge technology and industry-leading customer support, has seen the company go from strength to strength and become the gold standard in email and web security and the leading global provider of cloud-based security solutions for MSPs servicing the SMB market.
Phishing attacks on businesses are soaring, new malware variants are being released at record levels, and the current ransomware epidemic is threatening to derail businesses. Many SMBs lack the internal resources to block these threats and turn to MSPs to provide the security they need.
To cope with the increased demand, MSPs need solutions with 100% cloud-based architecture that seamlessly integrate into their existing centralized management systems and are easy to implement, use, and maintain. Ideally, those solutions need to be flexible, have a range of hosting options, be available in white-label form to take MSP branding, and also include generous margins. That is a big ask, and many solutions only tick a few of those boxes. However, TitanHQ’s suite of solutions include all those features and more.
TitanHQ also offers extensive sales enablement and marketing support, world-class customer service, and each MSP has a dedicated account manager, engineers, and a support team to help them maximize their sales opportunities and really grow their businesses.
As part of the celebration of the Q3, 2019 MSP growth, TitanHQ has launched a new initiative to ensure Q4 will be an even bigger success.
On October 22, TitanHQ announced a new disruptive price package for a SpamTitan Email Security and WebTitan DNS filtering bundle at an exclusive once-in-a-lifetime price. The initiative has been called Margin Maker for MSPs and is intended to ensure MSPs build profitability instantly in Q4, 2019.
The two solutions are provided in two private clouds, customized to meet MSPs email and web security needs, and secure the most common attack vectors – email and the web. The package includes advanced protection for email, including Office 365 environments, complimented by WebTitan DNS filtering to block web-based threats and implement content control for on-premises and remote workers. These solutions are naturally provided with extensive sales enablement and marketing support.
The aim is to make TitanHQ’s email and web security platforms even more appealing to MSPs and to encourage MSPs to offer both SpamTitan email security and WebTitan web filtering to their clients and maximize revenues.
One MSP that is already boosting its profits and achieving increased, reliable recurring monthly revenues is UK-based OpalIT. The MSP has bases in Newcastle and Edinburgh and a 6,000+ customer base. Prior to joining the TitanShield program, OpalIT was offering its clients firewall filtering and email filtering with Barracuda and Vade. The company has now switched to TitanHQ’s cybersecurity bundle and is pushing SpamTitan Email Security, WebTitan DNS filtering, and ArcTitan email archiving to its clients and is reaping the rewards.
“Opal IT moved to TitanHQ because of our MSP focused solutions, ease of deployments, extensive APIs functionality and the increased margin they’re now making. Our cybersecurity bundle solutions allow MSPs to provide their downstream customers with a layered defense approach” said Rocco Donnino, EVP Strategic Alliances, TitanHQ.
If you are a managed service provider, now is the perfect time to sign up with TitanHQ. Come and meet the TitanHQ channel team at the following MSP events to find out more about the TitanShield program for MSPs, OEMs, and service providers, and take advantage of the amazing new MSP package.

If you are unable to attend any of these events, be sure to give the TitanHQ team a call to find out more and take advantage of this exciting new and exclusive offer.
by titanadmin | Oct 21, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News, Spam Software
A new Stripe phishing campaign has been detected that uses fake warnings advising users about an invalid account to lure people into divulging their credentials and bank account information.
Stripe is an online payment processor used by many online firms on their e-commerce websites to accept payments from their customers. As such, the company is perfect for spoofing as many people will be aware that the company processes payments and will think it reasonable that they need to provide credentials and bank account information to ensure payments are processed.
The scam starts with a phishing email supposedly from the Stripe Support department. The email advises the customer that the information associated with their account is currently invalid. The message is sent as a courtesy notice warning the user that their account will be placed on hold until the matter is corrected. The user is asked to review their details to correct the issue. A button is included in the email for users to click to do this.
The emails contain spelling mistakes and questionable grammar, so are likely to be identified as suspect by vigilant individuals. Security awareness training often teaches employees to hover their mouse arrow over a hyperlink to find out the true URL, but in this campaign it will not work. The attackers have added a title to the HTML tag of the embedded hyperlink so when the mouse arrow is hovered over the “Review your Details” button, that text will be displayed instead of the URL.
If that button is clicked, the user will be directed to a seemingly legitimate Stripe login page. The login box is a clone of the real login page and a series of boxes will be displayed, each requiring different information to be entered, including bank account and contact information.
When the user is required to enter their password, regardless of what is typed, the user will be advised that they have entered an incorrect password and will be asked to enter the password again. The user is then directed to the legitimate Stripe login page to make it appear they have been on the correct Stripe website all along.
Anti-Phishing Demo
Protect your MSP clients with the newest zero-day threat protection and intelligence against anti-phishing, business email compromise and zero-day attacks with PhishTitan.
Free Demo
Similar tactics are used in countless other phishing campaigns targeting other well-known companies. The presence of spelling mistakes and grammatical errors in messages should tip off end users that the email is a phishing attempt, but all too often end users fail to notice these errors and click and divulge sensitive information.
One issue is a lack of cybersecurity training in the workplace. If employees are not trained how to identify phishing emails, it is inevitable that some will end up falling for these scams and will divulge their credentials. Those credentials can be used to gain access to bank accounts or email accounts, with the latter often used to conduct further phishing attacks on the organization. One email account breach can easily lead to dozens of breached accounts.
For example, a phishing attack on a U.S. healthcare provider started with a single phishing email and led to 73 email accounts being compromised. As for cybersecurity awareness training, this is often nonexistent. One recent study on 2,000 employees in the United Kingdom revealed three quarters had received no workplace cybersecurity training whatsoever.
Protected by Microsoft Office 365 Anti-Phishing Controls? Are You Sure?
One in every 99 emails is a phishing email, so it is important to ensure your defenses are capable of blocking those messages. Many businesses mistakenly believe they are protected against these emails by Microsoft’s Office 365 anti-phishing controls. While those measures do block spam email and some phishing messages, one recent study by Avanan has shown 25% of phishing attacks sneak past Office 365 defenses and are delivered to inboxes. For an average firm that means several phishing emails will reach end users’ inboxes every day. To ensure your business is protected against phishing attacks, additional anti-phishing controls are required on top of Office 365.
Businesses can protect their Office 365 accounts against phishing by layering SpamTitan on top of Office 365. SpamTitan is an advanced anti-phishing and anti-malware solution that provides superior protection against phishing, malware, spear phishing, and zero-day attacks.
Heuristics rules are used to analyze message headers and these rules are constantly updated to include the latest threats. Bayesian analysis and heuristics are used to check message content, and along with machine learning techniques, new threats are blocked and prevented from reaching inboxes. Sandboxing is also used to assess email attachments for malicious code used to install malware in addition to dual-AV engines that scan for known malware.
These advanced measures ensure that Office 365 inboxes are kept free from malware and phishing emails. These advanced capabilities along with the ease of implementation and use and industry-leading customer support are why SpamTitan is the leading provider of anti-spam and anti-phishing solutions for SMBs and managed service providers that serve the SMB market.
For further information on SpamTitan, to book a product demonstration or set up a free trial, contact the TitanHQ team today.
by titanadmin | Oct 15, 2019 | Email Archiving, Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Spam Advice, Spam Software, Website Filtering

IT Nation Connect 2019, the ConnectWise conference for the IT professional community, will be taking place on October 30, 31, and November 1 at the Hyatt Regency in Orlando, Florida.
The event is the leading conference for companies that sell, support, and service technology and is focused on helping attendees build a strong business and achieve long-term success. Attendees will gain practical advice from experts in the IT Nation community and will have the opportunity to build meaningful business connections and learn how to work on their businesses.
This year’s topics for the session tracks are mergers & acquisitions, growth & scalability, talent development & leadership, service delivery & customer success, sales & marketing, and security.
Security is a key focus of IT Nation Connect 2019. The event will provide opportunities to discover how security frameworks and IT solutions can help you bulletproof your business and protect your clients’ networks from cyberattacks. Attendees will also gain deep insights into the current state of security in the MSP space.
Leading security experts will be discussing the steps that the government is taking to combat cyber threats, the lessons the government and private firms have learned, and how security experts see the threat landscape evolving over the coming year.
Founders and CEOs of the most successful MSPs and IT firms will explain what it is like to be a trailblazer, how they achieved their successes, the mistakes they made on the way, and what the future holds for the IT Nation community.
More than 80 thought leaders, ConnectWise partners, and ConnectWise colleagues will taking over 130 educational, networking and panel sessions and will be sharing success stories, best practices, and the lessons they have learned to help attendees succeed and grow their businesses.
The conference offers an exceptional opportunity for learning, networking, and discovering technology solutions that can save you time, money, and boost the profitability of your business. Such an important event for the IT community is not to be missed.
TitanHQ will be attending the event to explain why TitanHQ is the global leader in cloud-based email and web security solutions for MSPs servicing the SMB market, the advantages of doing business with TitanHQ, and how TitanHQ solutions can help you better protect your environment and those of your clients from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
TitanHQ Marketing Director Dryden Geary, Sales Director Conor Madden, and Inside Sales Executive Peter Cooke will explain the benefits of the TitanShield program for MSPs, OEMs, technology partners, and Wi-Fi providers and show you just how easy it is to incorporate SpamTitan email security, WebTitan DNS filtering, and ArcTitan email archiving into your security stacks.
If you are attending the event, be sure to make time to meet with TitanHQ and feel free to reach out in advance of the event if you have any questions.
by titanadmin | Oct 11, 2019 | Email Archiving, Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Spam Software, Website Filtering
The 2019 Canalys Cybersecurity Forum will be taking place in Barcelona on October 16-17, 2019. The event is the only independent conference dedicated to the cybersecurity channel and is one of the most important events of the year for managed service providers (MSPs).
The event provides an incredible opportunity for MSPs looking to enhance their security stacks, provide greater value, and better protect their clients from increasingly sophisticated security threats. Attendees will have the opportunity to have 1:1 meetings with more than 700 established and new partners and discover best practices to adopt to get the most out of their cybersecurity solutions.
The event is also a must for MSPs who have yet to start offering managed security services as it will allow them to form new partnerships with Europe’s best cybersecurity solution partners who will help them grow their businesses significantly over the coming year.
Leading cybersecurity vendors will be taking thought-crunching sessions and sharing their knowledge to help partners succeed. Attendees will be able to engage in intense debates and interact with some of the brightest minds in the field of cybersecurity. Questions can be posed in multi-vendor theatre panels to get the answers from the leading cybersecurity solution providers in the EMEA region.
Highlights of this year’s event include panels, theatre and keynotes exploring the re-imaging of the idea of solutions, generalist vs. specialist in the cybersecurity channel, the next catalyst that will drive security sales, and how the role of the CSO is evolving in the hybrid IT world.
Canalys analysts will also be providing keynote speeches and sharing their insights into the current threat landscape and some of the burning issues of the moment. The event will also see Canalys name the new Threat Fighter and MSSP winners in the Canalys Channel Partner Awards.

TitanHQ Sales Director, Conor Madden
The event provides an amazing opportunity for networking with more than 200 channel partner delegates in attendance. New alliances can be formed and along with the knowledge gained, attendees will be able to make important decisions that will have a major positive impact on growth for the coming year.
TitanHQ is a proud sponsor of the 2019 Canalys Cybersecurity Forum and the team will be on hand to answer questions and explain why TitanHQ is the global leader in cloud-based email and web security solutions for the MSP that services the SMB market.

TitanHQ Strategic Alliance Manager, Marc Ludden
At the event you will be able to discover the considerable benefits of using SpamTItan email security, WebTitan DNS filtering, and ArcTitan email archiving to solve your clients security issues, better protect them from cybersecurity threats, and help them achieve their compliance objectives… and how easy TitanHQ makes this for MSPs.
TitanHQ Sales Director Conor Madden will be a panelist at the event and will be answering questions from attendees on email security, web security, email archiving and how to get the most out of TitanHQ’s cybersecurity solutions for MSPS and SMBs.
Marc Ludden, TitanHQ’s Strategic Alliance Manager, will also be attending and meeting with enterprise-level clients and major MSPs and ISPs to help them push TitanHQ products downstream to their customers, grow their businesses, and improve their bottom lines.
You can find out more about this one in a year opportunity here – Canalys Cybersecurity Forum 2019 – and feel free to reach out to TitanHQ in advance of the event.

If you are unable to attend this year’s Canalys event, TitanHQ will be on the road throughout October and November. Be sure to connect at one of the other fall 2019 events below:

by titanadmin | Oct 8, 2019 | Internet Security, Network Security, Website Filtering
If you are looking for a Cisco Umbrella alternative, you are not alone. TitanHQ has helped multiple businesses change from Cisco Umbrella to WebTitan Cloud. In most cases, the main reason why businesses seek a Cisco Umbrella alternative is to save money; but – depending on which Cisco Umbrella plan you subscribe to – WebTitan Cloud can also help better protect your business against web-borne threats and give you more control over Internet usage.
One of the challenges of evaluating a Cisco Umbrella alternate is that there are four versions of Cisco Umbrella – ranging in capabilities from a basic (and not entirely effectively) web filter to a top-of-the-range Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solution. This makes it difficult to conduct apples-for-apples comparisons especially with regards to price due to a lack of pricing transparency with both the licensing costs and the add-ons – some of which are necessary and one of which is mandatory.
Cisco Umbrella Review
The four versions of Cisco Umbrella are DNS Essentials, DNS Advantage, SIG Essentials, and SIG Advantage; and because the versions increase in capabilities as you go through the range, we have provided a synopsis of each version´s capabilities below.
DNS Essentials
DNS Essentials is the entry-level version of Cisco Umbrella. It blocks websites known to be harboring malware and published to conduct phishing attacks, blocks or allows Internet access by domain or category, and enables system administrators to create user policies and view activity reports – albeit at an additional cost if you integrate DNS Essentials with (for example) Active Directory.
The big problem with the DNS version of Cisco Umbrella is that it does not decrypt and inspect the content of encrypted websites. Therefore, if a website is not yet known to be harboring malware – or contains adult content that would normally be blocked by category – the filter will not be able to identify the content and the website will evade detection as a malicious or harmful website.
DNS Advantage
This version of Cisco Umbrella is more advanced than the entry-level version inasmuch as it supports SSL decryption and inspection and will block websites and files based on anti-virus inspection. It also blocks direct-to-IP traffic such as command and control callbacks that bypass DNS filters and can be integrated with the Cisco Investigate console to analyze threats (at an additional cost).
However, like the DNS Essentials version, DNS Advantage only blocks websites by domain, rather than by URL. This can create issues if, for example, you want to prevent users wasting time reading the sports pages of an online newspaper but want to give the finance team access to the online newspaper´s money pages. The same limitation applies to “allow” lists. It´s either all or nothing.
SIG Essentials
The first of two Secure Internet Gateway (SIG) packages improves on the DNS packages by providing more granularity over Internet usage. This version also comes with a cloud firewall that can be configured to block or allow specific IPs, ports, and protocols, while the anti-virus engine can be configured to scan previously benign files to check for previously disguised threats.
The drawback of this solution is that it is not a complete Secure Internet Gateway solution without subscribing to multiple add-ons (for example, outbound traffic scans) or overcoming limitations on services such as cloud storage scans. It is also important to be aware there is a mandatory charge for onboarding (applies to all versions) and an extra charge for priority technical support.
SIG Advantage
SIG Advantage has been acknowledged as a leading SASE solution by Gartner´s Magic Quadrant and this version of the Cisco Umbrella includes almost everything that is an add-on in other versions (except onboarding and technical support). Furthermore, you can enhance the capabilities of the SASE solution by taking advantage of Cisco Talos Incident Response (at a cost).
If there is an issue with this version, it is that it includes many features and capabilities that may exist in other security solutions already being used by the business (i.e., Microsoft Sentinel, Amazon Security Lake, etc.). Additionally, if the business does not have the technical abilities in-house to take advantage of all the capabilities, you won´t see a good ROI from SIG Advantage.
Cisco Umbrella Licensing
Each of the versions has a subscription-based licensing structure – the price of which varies according to the number of users, the length of the subscription, and the location of the business. The cost of add-ons is also calculated in the same way, offering economies of scale to larger companies in the “right” area who subscribe for the maximum five years.
Generally, the cost of Cisco Umbrella licensing has to be paid all-upfront, although some resellers allow monthly, quarterly, or annual payments. Additionally, while you might be able to get a better deal from resellers, you have to be sure that the deal you are getting includes all the add-ons you require to filter the Internet securely and effectively.
How Much Does Cisco Umbrella Cost?
Due to there being four different version of Cisco Umbrella, multiple add-ons, and a lack of pricing transparency it is impossible to answer the question how much does Cisco Umbrella cost. Some resellers advertise the DNS Essentials version with prices starting from $1.50 per user per month (for > 25,000 users/5-year subscription), but it is not possible to determine what this price includes.
Anecdotal evidence suggests the cost of the DNS Advantage version including mandatory onboarding and technical support is $2.70 per user per month for a business with 100 to 499 users. Even if other add-ons are included in the price, this still seems a little high compared with a Cisco Umbrella alternate such as WebTitan for which the equivalent cost per user per month id $1.58.
Is Cisco Umbrella Pricing Negotiable?
Although few businesses reveal how much they are paying for Cisco Umbrella, there does appear to be a range of prices published in user forums and comment boxes that imply you can get a discount off Cisco Umbrella pricing if you negotiate hard enough. What´s not clear is whether any discount off Cisco Umbrella pricing is from Cisco directly or from resellers.
Resellers is probably the best way to go if you are looking to protect a large number of users because resellers have profit margins they will likely be prepared to trim to get the business. Additionally, you can also play one reseller against another. However, beware of “introductory offers”, as the price will increase significantly when the time comes to renew the subscription.
Can the Cisco Umbrella Price be Justified?
It depends on what your business needs. If, for example, you compare the anecdotal price of the DNS Advantage version against a Cisco Umbrella alternative such as WebTitan, you could save around 40% by switching to WebTitan. Even if you negotiate a deal for DNS Advantage, the version of Cisco Umbrella you get is still going to lack granular filtering to effectively control Internet usage.
However, if your business needs all the bells and whistles of the SIG Advantage version of Cisco Umbrella – and none of the SASE solution´s capabilities are duplicated in existing security solutions – you may feel the Cisco Umbrella price is justified. However, we would strongly suggest researching what else is available before committing to a long term subscription.
WebTitan Cloud: An Ideal Cisco Umbrella Alternative
Cost is not the only consideration when looking for a Cisco Umbrella alternative – you need to sure that your DNS filtering and Internet security solution is providing you with maximum protection against web-borne threats and maximum control over Internet usage. You can be assured of both with WebTitan Cloud.
For example, rather than updating threat databases retrospectively as some solutions do, WebTitan Cloud´s threat database is updated in “real-time” to mitigate the risk of emerging threats evading detection. Additionally, WebTitan Cloud includes “Zero-Minute” protection against emerging phishing threats.
With regards to maximum control over Internet usage, WebTitan Cloud allows system administrators to apply acceptable usage policies by user, group, department, or location. Policies can also be applied by time of day, or – for schools – by school year to ensure students only have access to age-appropriate content.
Finally, WebTitan Cloud has been developed to be easy to implement, configure, use, and maintain. We aim for minimal administrative overhead, but there will naturally be times when things don’t go according to plan. In the event of a problem, all customers benefit from world class support at no extra cost (and in no priority order).
WebTitan Cloud Benefits for MSPs
One of the features of WebTitan Cloud that is particularly attractive to MSPs is the ability to host the solution locally within their own environment. Most businesses will choose to host WebTitan Cloud with TitanHQ, but the option is available if this suits you better. MSPs can also be supplied with WebTitan Cloud in white label format for rebranding and reselling.
- Transparent pricing – including monthly billing
- Multiple hosting options, including within your own data center
- Product can be supplied in white label format for rebranding
- No monthly minimums or yearly commitments
- The product can scale to meet your needs (and shrink too if needed)
- Extensive suite of customizable reports
- Easy integration into existing security and customer management systems
- World-class customer support included in the cost
- Generous margins for MSPs
- Access to an extensive library of support materials
Book a Free Web Filtering Demo to Find Out More
If you have any questions about WebTitan Cloud, would like information on how you can switch from Cisco Umbrella, or would like a product demonstration, complete the form below and one of the WebTitan team will be in touch to organize a convenient time for your free no-obligation demo.
The demo will not only show how easy it is to set up WebTitan Cloud, but how effective it is at blocking web-borne threats and helping your business control Internet usage. The opportunity also exists to take advantage of a free trial of WebTitan Cloud to evaluate its potential as a Cisco Umbrella alternative in your own environment.
by titanadmin | Oct 7, 2019 | Email Scams, Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam
The collapse of the package holiday operator Thomas Cook left thousands of holidaymakers stranded, hundreds of thousands of holiday bookings have been cancelled, and more than 9,000 staff have lost their jobs. The company and other UK firms in its group have been forced into compulsory liquidation and cybercriminals have been quick to take advantage. Dozens of Thomas Cook-related domains were registered following the collapse of the firm and several Thomas Cook phishing scams have been detected.
Customer that have incurred out-of-pocket expenses as a result of the collapse of the company and anyone who has paid for a package holiday that has been cancelled may be entitled to a refund or compensation. That has given scammers the perfect opportunity to launch phishing attacks seeking bank account an credit card information.
Customers who have booked Thomas Cook holidays are protected under the ATOL scheme and refunds are being processed by the Civil Aviation Authority, which has set up a subdomain on its website – thomascook.caa.co.uk – where customers can submit claims for refunds. More than 360,000 holidays have been booked for more than 800,000 holidaymakers, who are entitled to refunds. More than 60,000 customers submitted refund forms on the first day that the website was set up and claims for out-of-pocket expenses are being processed by travel insurance firms. The CAA has stated that it will take 60 days for the refunds to be issued.
Anyone who has yet to submit their claim should exercise caution as there are multiple phishing scams being conducted offering money back on canceled holidays, reimbursement of out-of-pocket expenses, compensation, and fake updates on the status of refund claims. Any email received in relation to Thomas Cook should be treated as a potential scam.
Scams may be conducted with the aim of spreading malware or ransomware. Malicious code is contained in file attachments that trigger a malware download when the attachment is opened. However, far more common in situations when people are demanding refunds is to send phishing emails containing hyperlinks to malicious websites. Those websites require sensitive information such as credit card information and bank account details to be entered. Scammers are well aware that in order for refunds to be processed, bank account information would be required and phishing forms have been set up on fake Thomas Cook domains to do just that.
While there may be some giveaways that emails are not genuine – spelling mistakes and grammatical errors – some Thomas Cook phishing scams are virtually impossible to distinguish from genuine communications. Banks have also been notifying customers by email, which has presented scammers with even more opportunities to hoodwink Thomas Cook customers. There have also been reports of former employees being targeted by scammers offering compensation.
The golden rule to avoid becoming a victim of Thomas Cook phishing scams is never to respond to a request in an unsolicited email. Attachments should not be opened, hyperlinks in emails should not be followed, and contact information included in the message body should not be used. Only use official channels such as the CAA website, and contact banks and travel insurance firms directly using verified contact information.
by titanadmin | Oct 3, 2019 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security
The cost of a ransomware attack can be considerable. Several attacks in the United States have seen payments of hundreds of thousands of dollars made for the keys to unlock the encryption. While those payments are certainly high, they are a fraction of the total cost of a ransomware attack which are usually several times the cost of any ransom payment.
Recovery without paying a ransom can be considerably more. The ransomware attack on the city of Baltimore saw a ransom demand of around $76,000 issued. Baltimore refused to pay. The attack is estimated to have cost the city at least $18.2 million.
The cost of that ransomware attack is high, but nowhere the cost of a suspected September 2019 ransomware attack on the Danish hearing aid manufacturer Demant. The firm experienced the attack on or around September 3, 2019. One month on and the firm still hasn’t recovered. In a recent message to its investors, the firm said the cyberattack would cost an estimated $80 million to $95 million, even though the company held a cyber insurance policy. Without that policy the bill would have been $14.6 million higher.
According to a notice on the firm’s website, it experienced “a critical incident” when its “IT infrastructure was hit by cyber-crime.” Ransomware was not mentioned by the firm although it has been reported as a ransomware attack by the Danish media.
The attack impacted its Polish production and distribution facilities, French cochlear implants production sites, Mexican production and service sites, its amplifier production site in Denmark, its entire Asia-Pacific network, and its enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
The firm is recovering its IT infrastructure and believes it will take a further two weeks for systems to be restored and business operations to approach normality. However, the effects of the attack are expected to be long-lasting.
The inability to access its systems across all these areas has caused major disruption to the company. The firm has been unable to supply its products, receive and process orders, and clinics in its network have had difficulty servicing end users.
Due to the limited information released it is unclear whether the company refused to pay a ransom, if the attackers could not supply valid keys to unlock the encryption, of if this was a sabotage attack akin to the NotPetya wiper malware attacks of 2017.
If this was a ransomware attack, the losses far exceed those of the Norwegian aluminum and energy company Norsk Hydro, whose ransomware attack cost the firm around $70 million, although it is a fraction of the cost of the NotPetya attacks on the shipping firm Maersk and FedEx, both of which caused losses of around $300 million.
These incidents all demonstrate just how damaging cyberattacks can be and the massive costs of recovery. As is typical, the cost of recovering its IT systems accounted for a small proportion of the total cost – around $7.3 million. The bulk of the losses were due to lost sales and the inability to process orders, which the company says make up around half of the estimated losses.
In a press release, the firm said in addition to the lost sales, “the incident has prevented us from executing our ambitious growth activities in some of the most important months of the year – particularly in the US, which is our biggest market.”
Malware, ransomware and wiper malware are most commonly delivered via a small number of attack vectors. All too often they start with a phishing email, exploitation of RDP, drive-by malware download, or the exploitation of unpatched vulnerabilities. The cost of preventative measures to block these attack vectors is pocket change by comparison to the cost of recovery from an attack.
TitanHQ cannot help businesses with securing RDP and patching promptly, but we can help businesses secure the email system and protect against drive-by malware downloads and other web-based attacks.
To find out more about how you can improve security against email- and web-based attacks, from a cost of as little as 90 cents per user per month, give our sales team a call.
The sales team will be happy to explain the ins and outs of our web and email security solutions, schedule product demonstrations, and help set you up for a free trial of our SpamTitan email security and WebTitan web security solutions and greatly improve your defenses against phishing, ransomware, malware, and wiper attacks.
by titanadmin | Sep 30, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
The Emotet botnet sprung back to life following a 4-month period of dormancy over the summer. The first campaigns, which involved hundreds of thousands of messages, used lures such as fake invoices, payment remittance advice notices, and statements to lure recipients into opening a malicious Word document, enabling content, and inadvertently launching a string of actions that result in the downloading of Emotet: One of the most dangerous malware variants currently being distributed via email.
It has only been a few days since those campaigns were detected, but now a new campaign has been detected. The latest malspam campaign also delivers Emotet but this time the lure is a free copy of Edward Snowden’s book – Permanent Record. The book is an account of Edward Snowden’s life that led up to his whistleblowing actions in 2013.
The campaign includes English, Italian, Spanish, and German language versions which claim to offer a free scanned copy of the former CIA staffer’s book. The English language version of the book is being distributed via email, so the attackers claim, because it is “Time to organize collective readings of Snowden book everywhere.” The email tells the recipient to “Go buy the book now, read it, share it, discuss it,” but conveniently a scanned copy is attached called Scan.doc.
As with the previous campaign, opening the attachment will display a Microsoft Product Notice – with appropriate logo – informing the user that Word has not been activated. The user is required to enable content to continue using Word and view the content of the document. At this point, all it takes is a single click to silently install Emotet. Once installed, Emotet will download other malware variants, including the TrickBot Trojan. Emotet is also being used to distribute ransomware payloads.
While the lures in the Emotet campaigns are regularly changed, they have all used malicious scripts in Word documents which download Emotet. The emails may be sent from unknown individuals or email addresses may be spoofed to make the emails appear to have come from a contact or work colleague.
The lures are convincing and are likely to fool may end users into opening the attachments and enabling content. For businesses, that can lead to a costly malware infection, theft of credentials, fraudulent bank transfers, and ransomware attacks.
Businesses can reduce risk by ensuring employees are told never to open email attachments in unsolicited emails from unknown senders, but also to verify the authenticity of any email attachment by phone before taking any action. It is also important to condition employees never to enable content in any document sent via email.
While end user security awareness training is essential, advanced anti-malware solutions are also required to prevent those messages from ever reaching inboxes.
SpamTitan includes DMARC authentication to block email impersonation phishing attacks and a Bitdefender-powered sandbox where suspicious email attachments can be safely executed and studied for malicious actions.
Along with a wide range of other content checks, including Bayesian analysis and greylisting, emails such as these can be blocked and prevented from being delivered to end users.
by titanadmin | Sep 30, 2019 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security
The dangers of ransomware attacks have been made abundantly clear to more than 5,000 patients in California whose medical records have been permanently lost as a result of a ransomware attack on their healthcare provider.
Simi Valley, CA-based Wood Ranch Medical experienced the attack on August 10, 2019 which saw ransomware deployed and executed on its servers which contained the medical records of 5,835 patients. The attack caused permanent damage to computer systems, and since backup copies of patient records were also encrypted, those records have been permanently lost. It is unclear how much the attackers demanded as payment for the keys and whether those keys would have worked had the ransom been paid.
Without patient records and faced with the prospect of having to totally rebuild the medical practice from scratch, the decision was taken to permanently close the business. Patients have been forced to find alternative healthcare providers and no longer have access to their medical records.
This is the second healthcare provider in the United States that has been forced out of business due to a ransomware attack. Brookside ENT and Hearing Center in Battle Creek, Michigan also closed its practice this year as a result of a ransomware attack. In that case, the practice owners refused to pay the ransom demand and patient records were permanently encrypted. The practice owners decided it was not possible to rebuild the practice from scratch and announced their early retirement.
It is unclear exactly how the ransomware was installed in each of these incidents, so it is not possible to determine what defenses could have been improved to prevent the attacks. However, in both cases, recovery of files from backups was not possible.
The purpose of a backup is to ensure that in the event of disaster, data will be recoverable. File recovery may be time consuming and downtime due to the attack likely to be expensive, but data will not be permanently lost.
In order to ensure file recovery is possible, backups must be tested. Files may be corrupted during the backup process and data restoration may not be possible. If backups are not tested to make sure files can be recovered, it will not be possible to guarantee file recovery in the event of disaster.
These incidents also highlight another fundamental rule of backing up. NEVER store the only copy of a backup on a networked or internet-connected computer.
In the event of ransomware attack, it is highly likely that backup copies on networked devices will be encrypted along with shadow volume copies. Ransomware encrypts these files to make sure the only way of recovering data is paying the ransom.
Even paying a ransom comes with no guarantee that data will be recoverable. Files may be corrupted through the encryption/decryption process – some data loss is inevitable – and the attackers may not be able to supply valid keys to decrypt files.
A good backup approach to adopt to prevent disasters such as these is a 3-2-1 strategy. 3 backups should be created, which should be stored on 2 different media, with 1 copy stored securely off site on a device that is not networked or connected to the internet.

by titanadmin | Sep 19, 2019 | Email Scams, Network Security, Phishing & Email Spam
After a quiet summer, the Emotet botnet is back in action. The threat actors behind Emotet are sending hundreds of thousands of malicious spam emails spreading the Emotet Trojan via malicious Word documents.
Emotet first appeared in 2014 and was initially a banking Trojan used to obtain credentials to online bank accounts. The stolen credentials are used to make fraudulent wire transfers and empty business accounts. Over the years the Trojan has evolved considerably, with new modules being added to give the malware a host of new features. Emotet is also polymorphic, which means it can change itself each time it is downloaded to avoid being detected by signature-based anti-malware solutions. Up until the start of 2019, more than 750 variants of Emotet had been detected.
The latest iteration of Emotet is capable of stealing banking credentials and other types of information. It is also capable of downloading other malware variants, which has led to security researchers naming it ‘triple-threat malware,’ as it has been used recently to download the TrickBot Trojan and Ryuk ransomware. These three malware threats along with the scale of the operation make Emotet one of the most dangerous threats faced by businesses. It is arguably the costliest and most destructive botnet ever seen.
Last summer, Emotet activity was so high and the threat so severe that the Department of Homeland Security issued an alert to all businesses in July 2018 warning them of the threat. That warning was mirrored by the UK National Cyber Security Center which published its own warning about the malware in September 2018. Activity remained high well into 2019, but suddenly stopped at the start of June when command and control server activity fell to next to nothing.
The hiatus in activity was only brief. Researchers at Cofense Labs discovered its command and control servers had been activated again in late August and a massive spamming campaign commenced on September 16 using bots in Germany. The campaign was initially focused on businesses in the United States, Germany, and United Kingdom but the campaign has now spread to Austria, Italy, Poland, Spain, and Switzerland.
After being downloaded, Emotet spreads laterally and infects as many devices as possible on the network. Email accounts on infected machines are hijacked and used to send further spam emails to all contacts in the account. Finally the malware downloader module is used to a secondary and often tertiary malware variant.
The latest campaign uses Word documents containing malicious macros, which launch PowerShell scripts that fetch the Emotet Trojan from a variety of different compromised websites, many of which are running the WordPress CMS.
The campaign uses a variety of lures including invoices, payment remittance advice, and statements, the details of which are contained in Word documents that require content to be enabled to view the document content.
Upon opening the document, the user is requested to accept the Office 365 license agreement. Failure to enable content, so the document claims, will result in Microsoft Word features being disabled.
This campaign includes personalized subject lines including the recipients name to increase the likelihood of a user taking the requested action. Genuine email thread are also hijacked to make it appear that the user has already been communicating with the sender of the email. Around a quarter of attacks use hijacked email threads. Data from Cofense indicates emails are being sent from 3,362 hijacked email accounts from 1,875 domains.
It is currently unclear whether Ryuk ransomware is being distributed in this campaign. Several researchers have confirmed that TrickBot is being downloaded as a secondary payload.
The key to blocking attacks with polymorphic malware is to implement layered defenses, including an advanced spam filtering solution, anti-virus software, and web filter. It is also important to ensure that the staff is made aware of the threat of attack and the types of email that are being used to spread the Trojan.
by titanadmin | Sep 19, 2019 | Industry News, Spam News, Spam Software
G2 Crowd, the independent peer-to-peer business software review site, has published its G2 Crowd Grid® Summer 2019 Report for Cloud Email Security. For the third consecutive quarter, SpamTitan has been named the leading cloud email security provider having been awarded the highest score for customer satisfaction.
G2 Crowd is the largest tech marketplace for businesses. The site attracts more than 3 million visitors and contains more than 843,500 reviews from verified software users. The reviews and Grid Reports are relied upon by countless businesses to help them make better software buying decisions.
Each quarter, G2 Crowd produces Grid reports that highlight the key players in different software categories. The G2 Crowd Grids are used to rank software solutions based on market presence and user satisfaction and categorize each as wither a niche player, contender, high performer, or leader. To be named a leader, a product must have a strong market presence and high user satisfaction level.
Market presence is determined by the size of the company, its social impact, and market share. The user satisfaction score is calculated from amalgamated reviews from verified users of the software.
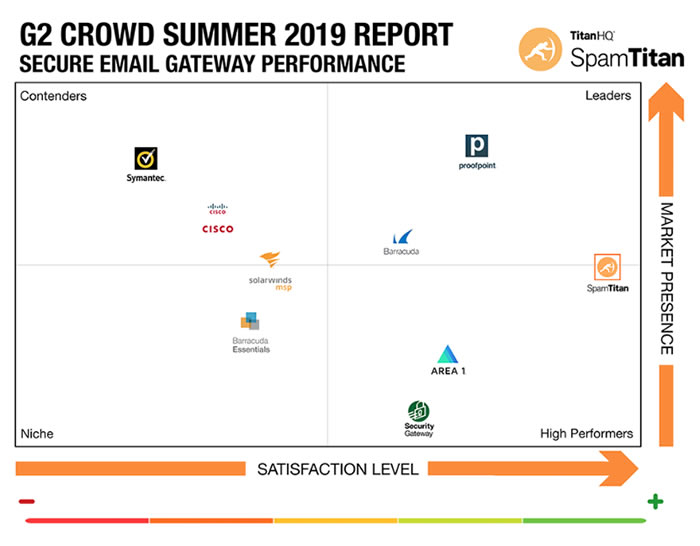
User reviews are important when choosing a software solution. If the software is difficult to use, fails to live up to expectations, or does not provide the required functionality, staff will avoid using it as much as possible. For a security solution that is particularly bad news.
The Summer 2019 report includes 9 email security solutions. SpamTitan achieved the highest overall customer satisfaction score – 97% – of all nine solutions by some distance. The next highest customer satisfaction scores were for Proofpoint Email Security & Protection (75%), Area 1 Security (69%), and Barracuda Email Security Gateway (61%).
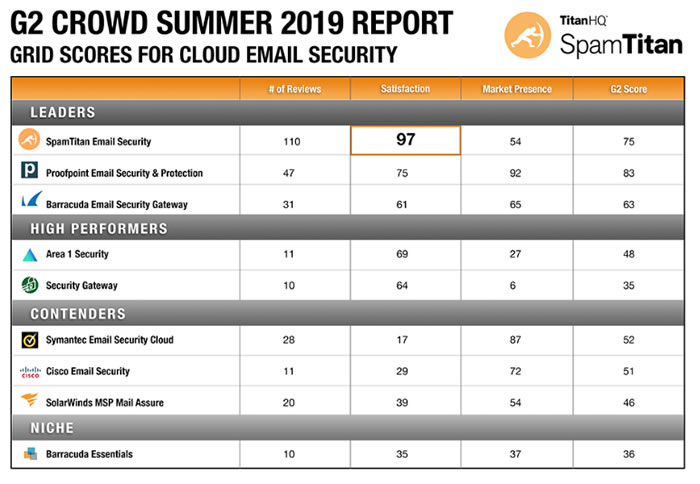
In addition to the Grid reports, amalgamated scores are included for six different customer satisfaction criteria: Ease of setup, ease of use, ease of admin, ease of doing business, quality of support, and meets requirements. Once again, SpamTitan topped the list with the highest score for ease of setup (92%) and ease of use (92%) and was one of only two solutions that achieved scores of over 90% in each of the six categories.
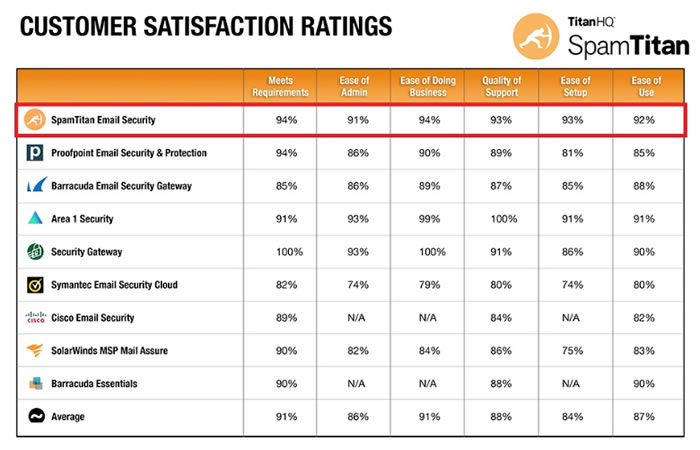
“The overwhelmingly positive feedback on G2 Crowd from users of SpamTitan is indicative of our commitment to ensuring the highest levels of customer success,” said Ronan Kavanagh, CEO, TitanHQ. “That’s an incredible achievement for a product that is significantly more affordable than the market leaders.”
by titanadmin | Sep 16, 2019 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security, Spam Software, Website Filtering
This fall, TitanHQ will be attending several Managed Service Provider (MSP) events and trade shows throughout Europe and the United States.

TitanHQ has been developing innovative cybersecurity solutions for MSPs for more than two decades and all solutions have been created with MSPs firmly in mind. By involving MSPs in the design process, TitanHQ has been able to ensure that its products incorporate features to make life easier for MSPs, such as easy integration into MSPs management systems through the use of APIs to features rarely found in cybersecurity products – such as full white label versions ready for MSP branding and the ability to host the solutions within MSPs own environments.
Trade shows give the TitanHQ team the opportunity to meet face to face with prospective clients to discuss their email and web security needs and get face to face feedback from current customers that have already integrated TitanHQ products into their technology stacks.
The TitanHQ team kicked off the fall schedule of trade shows on September 12 at the Taylor Business Group BIG 2019 Conference at the Westin Hotel in Chicago, where members got to meet the TitanHQ team to discuss the new TitanShield program and discover how TitanHQ products can improve security for their clients while saving MSPs time and money.
At the same time, TitanHQ was at the CloudSec Europe 2019 Conference in London demonstrating WebTitan Cloud, SpamTitan Cloud, and ArcTitan to MSPs and cloud service providers.
If you were unable to attend either of these two events or did not get the chance to meet with the team, all is not lost. The fall schedule has only just commenced and there are still plenty of opportunities to meet the team to discuss your requirements and find out how TitanHQ products can meet and exceed your expectations.
Trade Events Attended by TitanHQ – Autumn, 2019
| Date |
Event |
Location |
| September 17, 2019 |
Datto Dublin |
Dublin, Ireland |
| September 18, 2019 |
MSH Summit |
London, UK |
| October 6-10, 2019 |
Gitex |
Dubai, UAE |
| October 7-8, 2019 |
CompTIA EMEA Show |
London, UK |
| October 16-17, 2019 |
Canalys Cybersecurity Forum |
Barcelona, Spain |
| October 21-23, 2019 |
DattoCon Paris |
Paris, France |
| October 30, 2019 |
MSH Summit North |
Manchester, UK |
| October 30, 2019 |
IT Nation Evolve (HTG 4) |
Florida, USA |
| October 30, 2019 |
IT Nation Connect |
Florida, USA |
| November 5-7, 2019 |
Kaseya Connect |
Amsterdam, Netherlands |
If you plan on attending any of the above events this fall, be sure to come and visit the TitanHQ team and feel free to reach out ahead of the events for further information.
Rocco Donnino, Executive Vice President-Strategic Alliances, LinkedIn
Eddie Monaghan, MSP Alliance Manager, LinkedIn
Marc Ludden, MSP Alliance Manager, LinkedIn
Dryden Geary, Marketing Director
by titanadmin | Sep 11, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
Google has acknowledged a vulnerability in the Google Calendar app is being exploited by cybercriminals to inject fake and malicious items into Google Calendar.
Several Google Calendar phishing campaigns were detected over the summer of 2019 which were exploiting this flaw. The campaigns saw Google Calendar spam sent to large numbers of users, including invites to events and other requests and special offers that popped up on unsuspecting users’ screens.
These notifications contained links to webpages where users could find out more information about the events and special offers. If events were accepted, they would be inserted into users’ calendars and would trigger automatic notifications. The offers and invites would keep on appearing until the users’ clicked the link. Those links directed users to phishing pages where credentials were harvested.
Some of the scams required credit card information to be entered, others required the user to login using their Office 365 credentials. Links could also direct users to webpages where drive-by malware downloads take place.
Most people are aware of the threat of phishing emails, malicious text messages, and social media posts that harvest sensitive information, but attacks on calendar services are relatively unheard of. Consequently, many users will fail to recognize these notifications and calendar items as malicious, especially when they appear in a trusted app such as Google Calendar.
Unfortunately, these attacks are possible because in the default setting, anyone can send a calendar event to a user. That event will be inserted into the user’s calendar and will automatically trigger notifications, as is the case with legitimate events.
In addition to events, messages can include special offers, notifications of cash prizes, alerts about money transfers, and all manner of other messages to entice the user to click a malicious link and disclose sensitive information or download malware.
Google Calendar is not the only calendar service that is prone to these attacks. Apple users have also been targeted, as have users of other calendar apps.
How to Block Google Calendar Phishing Attacks
Recently, a Google employee acknowledged the increase in ‘calendar spam’ and confirmed action was being taken by Google to address the problem.
In the meantime, users can prevent these spam and phishing messages from appearing by making a change to the app settings. Users should navigate to Event Settings > Automatically Add Invitations, and select the option “No, only show invitations to which I’ve responded” and uncheck the “show declined events” option in View Options.
Businesses should also consider including Google Calendar phishing scams in their security awareness training programs to ensure employees are aware that phishing attacks are not limited to email, text message, telephone calls, and social media posts.
by titanadmin | Sep 10, 2019 | Email Scams, Phishing & Email Spam
Business email compromise scams are now the leading cause of cyberattack-related losses. Billion are being lost each year and there are no signs of the attacks abating. In fact, it has been predicted that the number of attacks and losses will continue to increase.
Around 1% of global GDP is lost to cybercrime each year and that figure is increasing rapidly. Currently, around $600 billion is lost each year to cybercrime. A FinCEN report from July 2018 shows that suspicious activity report (SAR) filings have increased from $110 million per month in 2016 to $301 million per month in 2018 and Cybersecurity Ventures predicts losses will increase to $6 trillion globally by 2021. According to the FBI, more than $1.2 billion was lost to business email compromise scams in the United States alone in 2018.
Business email compromise (BEC) scams involve the impersonation of an executive or other individual, whose compromise email account is used to send fraudulent wire transfer requests. A variation sees a business associate of the company spoofed and requests sent demanding outstanding involves be paid. The latter is now more common than attacks spoofing the CEO.
BEC attacks usually start with a spear phishing attack to obtain email account credentials. Once email credentials are compromised, the account is used to send messages to other individuals in the organization, such as employees in the payroll, HR, or finance department. Since the emails come from a trusted source within the organization and the wire transfer requests are not unusual, payment is often made.
A successful attack can see sizable wire transfers made to accounts controlled by the attackers. Payments are often for tens of thousands of dollars or, in some cases, millions of dollars. A recent attack on a subsidiary of the car manufacturer Toyota Boshoku Corporation saw a fraudulent transfer of $37 million made to the attackers.
While that incident stands out due to the scale of the loss, fraudulent transfers of millions of dollars are far from unusual. In many cases, only a small percentage of the transferred funds are recovered. Since these attacks can be extremely profitable, it is no surprise that the so many cybercriminal gangs are getting in on the act and are conducting campaigns.
A new report from the insurer AIG shows BEC attacks are now the leading reason for cybersecurity-related insurance claims, having overtaken ransomware attacks for the first time. 23% of all cyberattack-related claims are due to BEC scams.
In the most part, these BEC attacks can be prevented with basic cybersecurity measures. AIG attributes the rise in claims to poor security measures at the targeted organizations. Investigations have uncovered numerous basic cybersecurity failures such as not providing security awareness training to employees, the failure to enforce the use of strong passwords, no multi-factor authentication, and poor email security controls.
If businesses fail to implement these basic cybersecurity measures, attacks are inevitable. Cyber-insurance policies may cover some of the losses, but many SMBs will not be in a position to make a claim. For them, BEC attacks can be catastrophic.
If you run a business and are concerned about your defenses against phishing, spear phishing, and BEC attacks, contact TitanHQ to find out more about effective cybersecurity solutions that can block BEC attacks.


 TitanHQ has announced a new partnership with Pax8. The partnership means Pax8 partners now have access to TitanHQ’s cloud-based email security solution – SpamTitan – and its DNS filtering solution, WebTitan.
TitanHQ has announced a new partnership with Pax8. The partnership means Pax8 partners now have access to TitanHQ’s cloud-based email security solution – SpamTitan – and its DNS filtering solution, WebTitan.










